108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

施行脑血管造影后皮层性视损伤的潜在危险因素:回顾性研究
Authors Yang Y, Zhang J, Li T
Received 9 May 2019
Accepted for publication 5 July 2019
Published 19 August 2019 Volume 2019:15 Pages 1013—1017
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S215158
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Deyun Wang
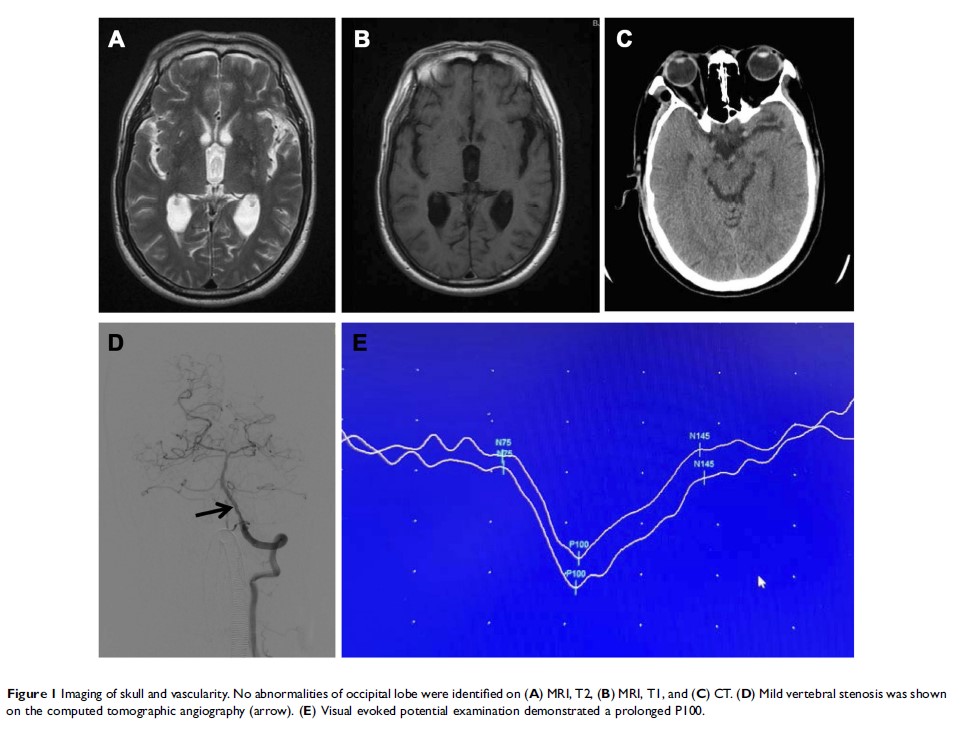
Background: Cortical visual impairment is an uncommon complication after cerebral angiography with an incidence of 0.3%-1.0%. Here we would like to investigate and discuss the potential risk factors of cortical visual impairment after cerebral angiography.
Methods: Based on the presence of post-operative cortical visual impairment, 4,528 patients who received cerebral angiography were split into two groups. The relevant risk factors were compared and analyzed between the groups.
Results: In the patient cohort, 11 cases exhibited post-operative cortical visual impairment (0.24%). In particular, seven patients presented with blurred vision and four presented with binocular blindness. Visual sensation of these patients recovered after the treatment. Our univariate analysis revealed that differences in age, weight, sex ratios, proportions of patients with hypertension, diabetes and hyperlipemia, and operation time were not statistically significant between the two groups (P >0.05). The multivariate analysis indicated that the dosage of contrast medium was the independent risk factor for post-operative cortical visual impairment.
Conclusion: Clinically, cortical visual impairment following cerebral angiography typically presented as blurred vision or complete blindness. We have identified the dosage of contrast medium as the most critical independent risk factor based on our study. Preventive strategies need to be implemented to avoid post-operative cortical visual impairment in this regard.
Keywords: cortical blindness, angiography, contrast agent