108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

ARHGAP25 在肺癌细胞中的肿瘤抑制作用
Authors Xu K, Liu B, Ma Y
Received 4 March 2019
Accepted for publication 19 June 2019
Published 19 August 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 6699—6710
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S207540
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Rachel Predeepa
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
Aim: Several Rho GTPase-activating proteins (Rho GAPs) have been proved to serve as tumor suppressors in diverse human cancers. Among them, ARHGAP25 has also been found to be associated with hematopoietic cells and regulate phagocytosis. Little is known about the role of ARHGAP25 in lung cancer cells.
Methods: Quantitative real-time PCR and Western blot were used to measure the expression levels of ARHGAP25. The ability of cell growth and mobility were measured by cell proliferation and Transwell assays. Chromatin immunoprecipitation and luciferase assay were conducted to identify the transcriptional regulation.
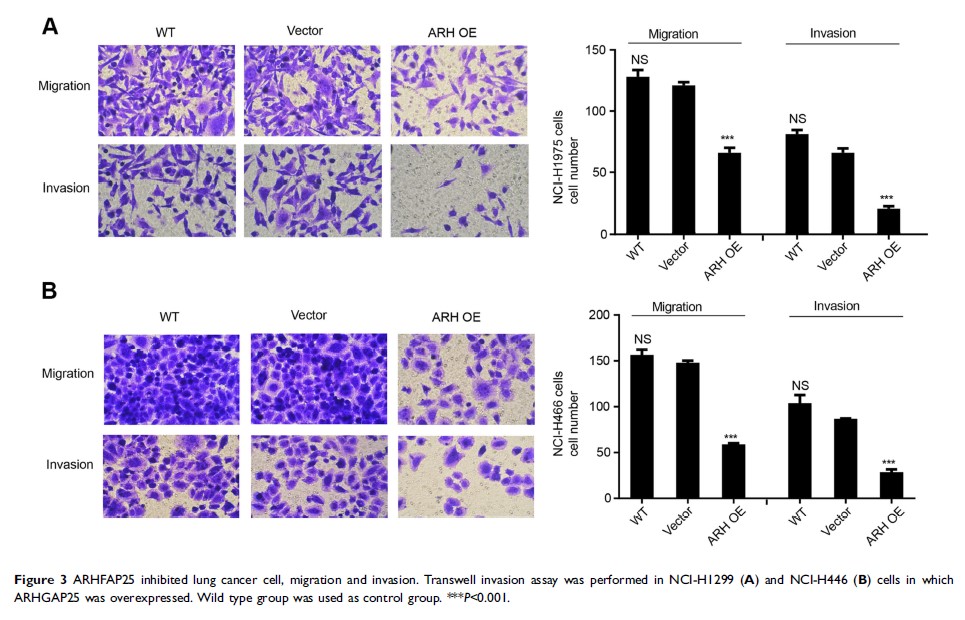
Results: Lung cancer tissues had much lower expression level of ARHGAP25 compared to non-cancerous specimens as well as for lung cancer cells. Cell growth and mobility were strongly reduced when ARHGAP25 was overexpressed. Further, significantly negative correlation between ARHGAP25 expression and Wnt signaling pathway was observed. Overexpression of ARHGAP25 reduced the expression of β-catenin and matrix metalloproteinase-7. ARHGAP25 knockdown effect of increased abilities of cell proliferation, migration and invasion could be reversed by adding XAV939 inhibitor. The promoter site of ARHGAP25 could be bound with HOXA4. HOXA4 could regulate the transcriptional activity of ARHGAP25.
Conclusions: This study suggests that ARHGAP25 may inhibit lung cancer cell growth, migration and invasion through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and its transcriptional activity can be regulated by HOXA4.
Keywords: ARHAGP25, Wnt signaling pathway, HOXA4, lung cancer, biological function