108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

抑制由 HPV16 致癌基因介导的糖酵解可以提高人宫颈癌细胞对 5-氟尿嘧啶的敏感性
Authors Ma D, Huang Y, Song S
Received 14 February 2019
Accepted for publication 24 July 2019
Published 19 August 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 6711—6720
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S205334
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Shreya Arora
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Federico Perche
Background: Human papillomavirus (HPV), the major cause of cervical cancer worldwide, is associated with infection of HPV (Oncogenic HPV). Cancer patients who develop drug resistance are resulted in failure of chemotherapy.
Objective: We investigated the mechanisms for the HPV E6/E7 oncoprotein-mediated 5-fluorouracil (5-Fu) sensitivity.
Methods: HPV-16 E6/E7 was transfected into human cervical cancer cell lines. Glycolysis rate was assessed. Xenograft model was established to examine the in vivo therapeutic effects of E6/E7 inhibition and 5-Fu treatments.
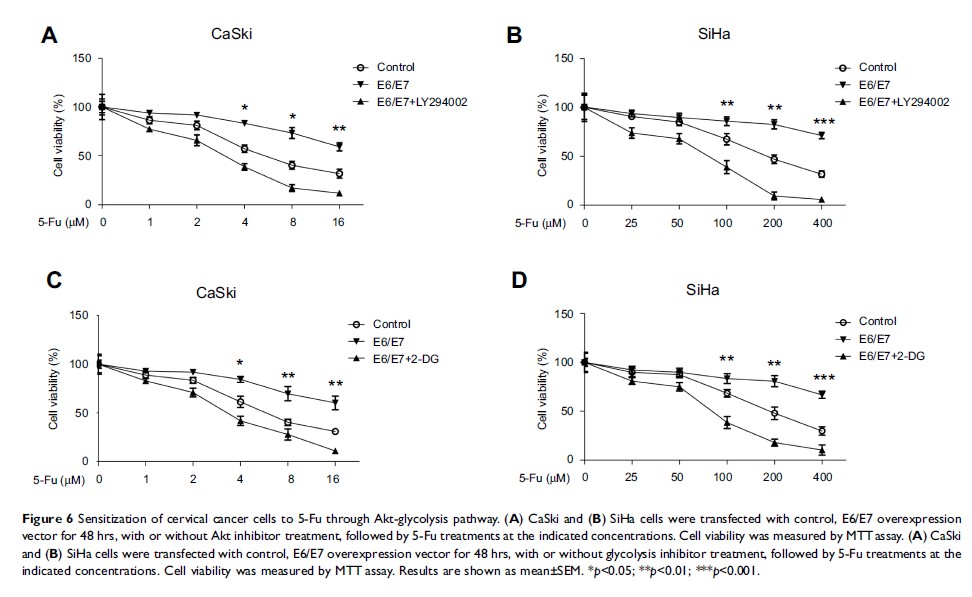
Results: The HPV-16 E6/E7 oncoprotein induces 5-Fu resistance in cervical cancer cells. Overexpression of E6/E7 renders CaSki and SiHa cells resistant to 5-Fu treatments. We found E6/E7 expressions were significantly upregulated in 5-Fu-resistant cells compared with parental cells. Moreover, the cellular glycolysis rate was significantly increased in 5-Fu-resistant cells. The glucose uptake, lactate production, and expressions of glycolysis enzymes were upregulated in 5-Fu-resistant cells. We report the E6/E7-mediated 5-Fu resistance was through upregulation of glycolysis pathway. Importantly, inhibition of E6/E7 by shRNA effectively decreased cellular glycolysis and overcame 5-Fu resistance using in vitro and in vivo xenograft model.
Conclusion: Our study contributed to understanding the molecular mechanisms for HPV E6/E7-mediated 5-Fu resistance and development of new therapeutic strategies against cervical cancer.
Keywords: human papillomavirus, Warburg effect, chemoresistance, 5-Fu, cervical cancer, HPV E6/E7