108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

白屈菜碱可增强乐伐替尼对肝细胞癌细胞的抗肿瘤作用
Authors Hou F, Guo L, Zheng K, Song J, Wang Q, Zheng Y
Received 9 May 2019
Accepted for publication 8 August 2019
Published 19 August 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 6685—6697
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S215103
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Rachel Predeepa
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Nicola Silvestris
Background: Lenvatinib is a newly approved molecular targeted drug for the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, the high cost associated with this treatment poses a huge financial burden on patients and the entire public health system. Therefore, there is an urgent need to develop novel strategies that enhance the antitumor effect of lenvatinib.
Methods: The antitumor effects of chelidonine or/and lenvatinib on HCC cell lines MHCC97-H and LM-3 were examined using the 3-[4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl]-2,5-diphenyl-2- H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. For the in-vivo investigation, the effect on subcutaneous or intrahepatic tumor growth in nude mice was also determined. The mRNA levels of epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT)-related factors were examined through quantitative polymerase chain reaction or Western blot.
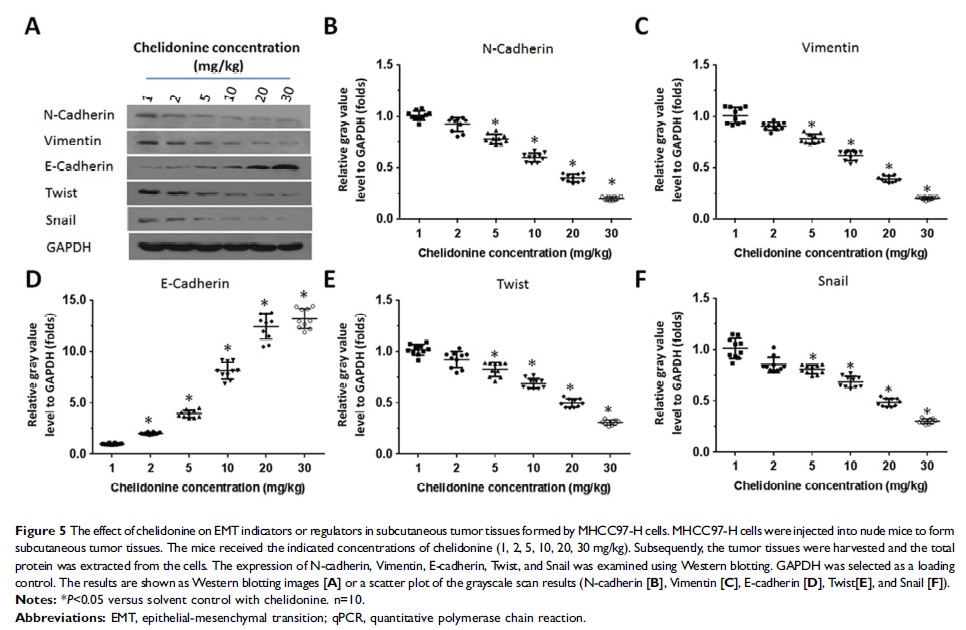
Results: In the present study, we found that treatment with chelidonine enhanced the apoptotic effect of lenvatinib on HCC cells and the in-vivo growth of HCC tumors in nude mice. Mechanistically, treatment with chelidonine increased the expression of epithelial indicator E-cadherin, whereas it decreased the expression of mesenchymal indicators N-cadherin and Vimentin. These findings suggest that chelidonine restricted the EMT in HCC cells.
Conclusion: Chelidonine inhibits the process of EMT and enhances the antitumor effect of lenvatinib on HCC cells.
Keywords: advanced hepatocellular carcinoma, lenvatinib, chelidonine, epithelial mesenchymal transition