108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

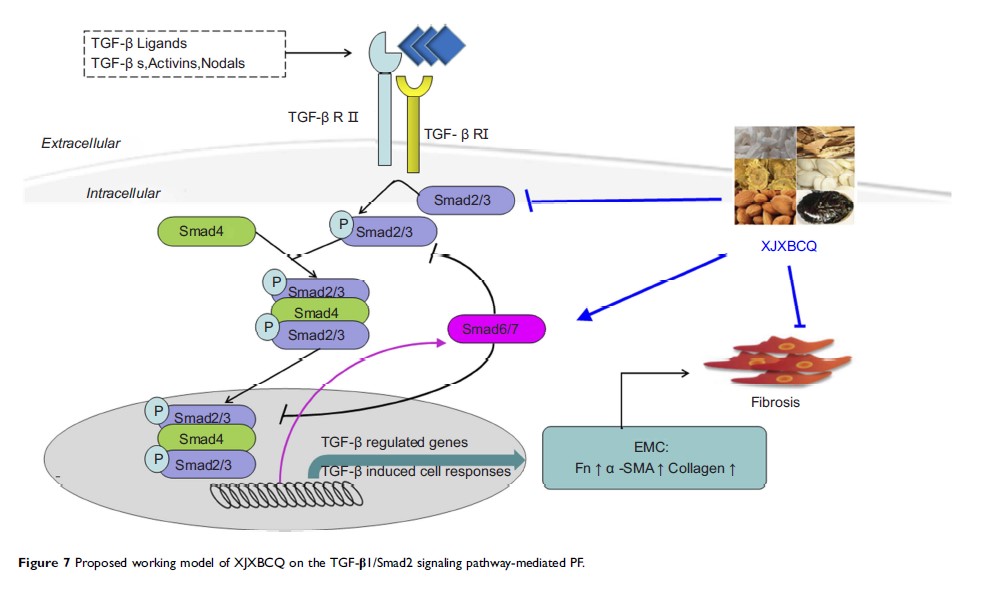
辛稼轩白承气汤的全部提取物通过 TGF-β/Smad 信号通路在体内和体外抑制肺纤维化
Authors Qin H, Wen HT, Gu KJ, Hu XD, Yang T, Yan XF, Ye TJ, Huo JL, Hu J
Received 27 August 2018
Accepted for publication 29 April 2019
Published 19 August 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 2873—2886
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S185418
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Qiongyu Guo
Purpose: Pulmonary fibrosis (PF) is a common clinical disease, which results in serious respiratory impairment. Xin Jia Xuan Bai Cheng Qi Decoction (XJXBCQ) is a traditional prescription commonly used in treating lung diseases. We investigate the effect of XJXBCQ against PF and its mechanism via the regulation of TGF-β1/Smad in vitro and in vivo.
Materials and methods: XJXBCQ was first extracted and probed for chemical characterization. An PF model in vitro and in vivo was established in rats and in MRC-5 cells. In bleomycin (BLM)-induced rats model, lung function such as peak expiratory flow (PEF), minute ventilation (MV) and hydroxyproline (HYP) were measured; histopathological changes of lung tissue and TGF-β1 in peripheral blood of rats were detected. TGF-β receptor, Smad2 and its phosphorylation expression were tested by Western blot assay in rats model. Then the effects of XJXBCQ on TGF-β1/Smad signal pathway were assessed by Western blot analysis in vitro, and IL-17A and IL-25 levels were evaluated by ELISA in vivo.
Results: Our results showed that XJXBCQ significantly enhanced the lung functions, such as PEF, MV and HYP, by reducing the expression level of lung inflammatory cytokine and the content and fibrosis of lung collagen. Moreover, XJXBCQ effectively inhibited TGF-β1, Smad2 and its phosphorylation expression, and the activation of Smad7 in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, XJXBCQ had an inhibitory effect on the α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and fibronectin (Fn) in vitro and downregulated IL-17A and IL-25 by inhibiting the activation of TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo. Further, XJXBCQ effectively inhibitied ventilation volume and peak expiratory content remodeling and hydroxyproline content through inhibition of TGF-βRⅡ, Smad2 and its phosphorylation expression, and activation of Smad7 in vivo.
Conclusion: XJXBCQ extract had an anti-PF effect in vitro and in vivo, which could be attributed to the inhibition of the expression of p-Smad2 and increase in the expression of Smad7 by regulating the TGF-β1/Smad activity.
Keywords: pulmonary fibrosis, lung inflammatory cytokines, transforming growth factor beta family, Smads family, Xin Jia Xuan Bai Cheng Qi decoction