109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Gal-3 和 MUC1 在大肠癌和结肠癌中的表达及意义
Authors Wang H, Wang L
Published Date July 2015 Volume 2015:8 Pages 1893—1898
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S83502
Received 25 February 2015, Accepted 6 May 2015, Published 27 July 2015
Approved for publication by Professor Daniele Santini
Objective: The objective of the present investigation was to explore the expression and significance of Gal-3 and MUC1 in colorectal cancer tissue and tissue adjacent to carcinoma.
Methods: In this study we collected colorectal cancer tissues and the tissues adjacent to carcinoma from 45 cases from the Colorectal Cancer Surgery Department of Zhengzhou People’s Hospital from December of 2009 to June of 2010. At the same time, this study also collected nontumor tissues adjacent to carcinoma from 20 cases as the control group. The expression of Gal-3 and MUC1 of these tissues was detected by using immunohistochemistry streptavidin-peroxidase method, and the correlation between colorectal cancer and expression of Gal-3 and MUC1 was analyzed.
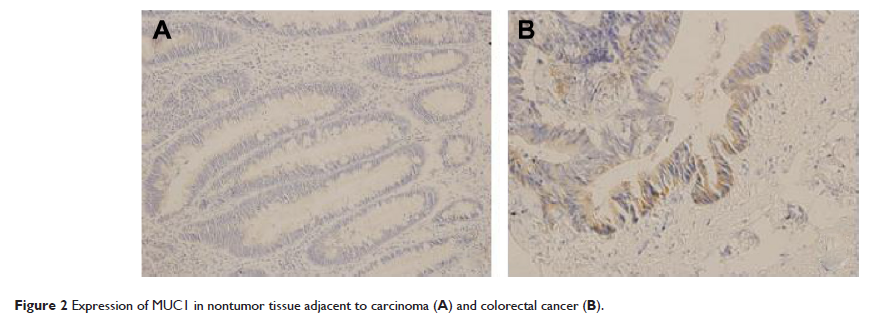
Results: The positive expression rates of Gal-3 in the tissues adjacent to carcinoma and colorectal cancer were 15.0% and 73.3%, respectively. The positive expression rate of Gal-3 in colorectal cancer was significantly higher than that in the tissue adjacent to carcinoma. The positive expression rate of Gal-3 of the patients without lymph node metastasis was 61.5% (16/26). The positive expression rate of Gal-3 in the patients with lymph node metastasis was 89.5% (17/19), and the difference was statistically significant (P =0.0363). The positive expression rates of MUC1 in the tissues adjacent to carcinoma and in colorectal cancer tissues were 0.0% and 54.5%, respectively. The positive expression rate of MUC1 in colorectal cancer tissues was significantly higher than that in the normal tissues adjacent to carcinoma (P <0.05); the positive expression rate of MUC1 in the patients without lymph node metastasis was 34.6% (9/26). The positive expression rate of MUC1 in the patients with lymph node metastasis was 84.2% (16/19), and the expression difference was statistically significant (P =0.0009).
Conclusion: The expression of Gal-3 and MUC1 was significantly higher than that in the nontumor tissue adjacent to carcinoma. There was a correlation between Gal-3 and MUC1 expression and lymphatic metastasis.
Keywords: immunohistochemistry, lymph node metastasis, invasion of tumor