108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

放射性特征:用于鉴别侵袭性和非侵袭性肺腺癌病例的非侵入性生物标志物
Authors Yang B, Guo L, Lu G, Shan W, Duan L, Duan S
Received 31 May 2019
Accepted for publication 30 July 2019
Published 19 August 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 7825—7834
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S217887
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Melinda Thomas
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Bilikere Dwarakanath
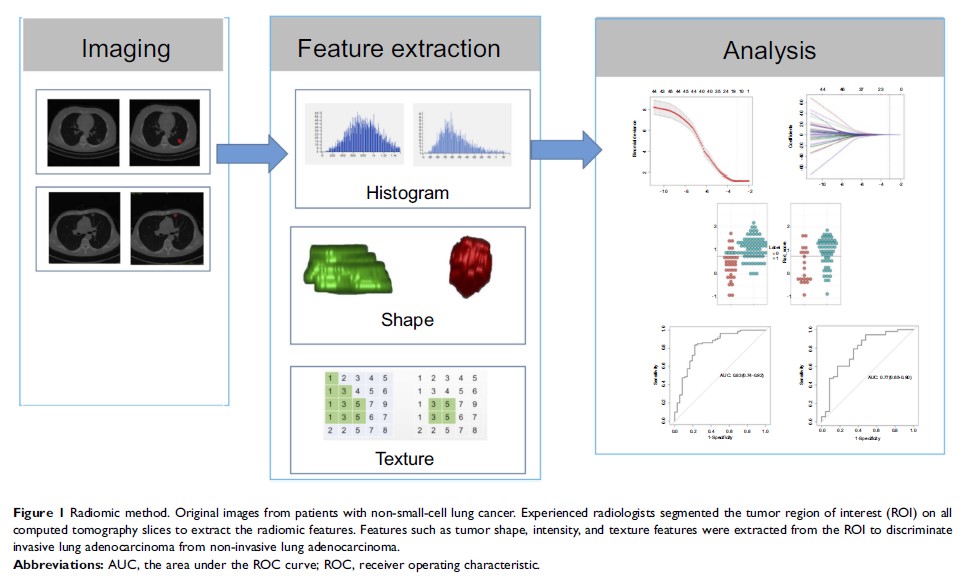
Purpose: We aimed to assess the classification performance of a computed tomography (CT)-based radiomic signature for discriminating invasive and non-invasive lung adenocarcinoma.
Patients and Methods: A total of 192 patients (training cohort, n=116; validation cohort, n=76) with pathologically confirmed lung adenocarcinoma were retrospectively enrolled in the present study. Radiomic features were extracted from preoperative unenhanced chest CT images to build a radiomic signature. Predictive performance of the radiomic signature were evaluated using an intra-cross validation cohort. Diagnostic performance of the radiomic signature was assessed via receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis.
Results: The radiomic signature consisted of 14 selected features and demonstrated good discrimination performance between invasive and non-invasive adenocarcinoma. The area under the ROC curve (AUC) for the training cohort was 0.83 (sensitivity, 0.84 ; specificity, 0.78; accuracy, 0.82), while that for the validation cohort was 0.77 (sensitivity, 0.94; specificity, 0.52 ; accuracy, 0.82).
Conclusion: The CT-based radiomic signature exhibited good classification performance for discriminating invasive and non-invasive lung adenocarcinoma, and may represent a valuable biomarker for determining therapeutic strategies in this patient population.
Keywords: lung adenocarcinoma, radiomics, biomarker, computed tomography