108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

tRNA 衍生片段 tRF-03357 促进高级别浆液性卵巢癌的细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭
Authors Zhang M, Li F, Wang J, He W, Li Y, Li H, Wei Z, Cao Y
Received 26 February 2019
Accepted for publication 16 July 2019
Published 16 August 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 6371—6383
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S206861
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Rachel Predeepa
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
Background: High-grade serous ovarian cancer (HGSOC) is one of the most common ovarian epithelial malignancies. tRNA-derived fragments (tRFs) have been identified as novel potential biomarkers and targets for cancer therapy. Nevertheless, the influence of tRFs on HGSOC remains unknown. This study aimed to identify HGSOC-associated tRFs and to investigate the function and mechanism of key tRFs in SK-OV-3 ovarian cancer cells.
Methods: The tRF profiles in HGSOC patients and controls were investigated using small RNA sequencing. Differentially expressed tRFs were verified by real-time PCR, and a key tRF was evaluated in function study.
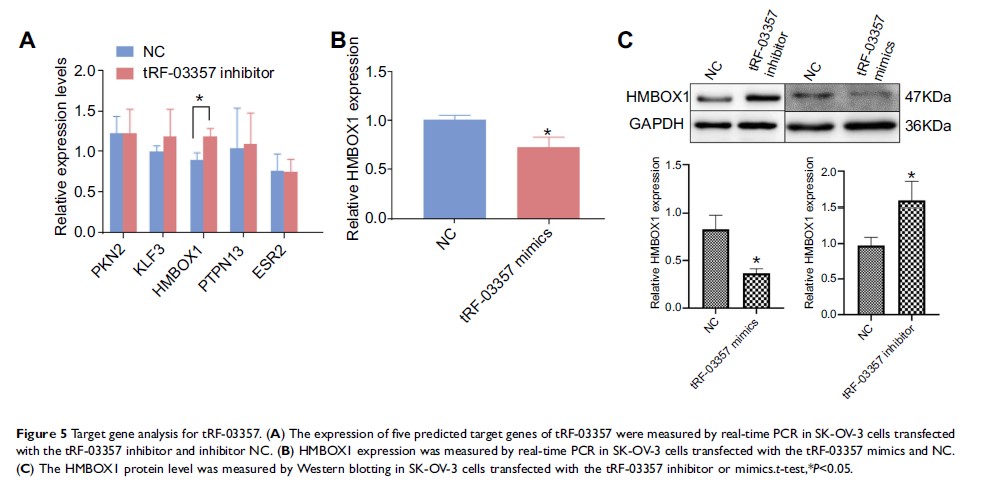
Results: A total of 27 tRFs were differentially expressed between HGSOC patients and controls. Differentially expressed tRFs were mainly involved in the functions of protein phosphorylation, transcription and cell migration and the pathway of cancer, MAPK and Wnt signaling pathways. Real-time PCR verified that tRF-03357 and tRF-03358 were significantly increased in the HGSOC serum samples and SK-OV-3 cells compared to their expression levels in the controls. Importantly, tRF-03357 promoted SK-OV-3 cell proliferation, migration and invasion. Moreover, tRF-03357 was predicted targeted and significantly downregulated HMBOX1.
Conclusion: This study suggests that tRF-03357 might promote cell proliferation, migration and invasion partly by modulating HMBOX1 in HGSOC.
Keywords: high-grade serous ovarian cancer, tRNA-derived fragments, migration, invasion, cell growth