108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

安非他替治疗晚期肺癌的疗效和安全性
Authors Shao L, Wang W, Song Z, Zhang Y
Received 16 February 2019
Accepted for publication 21 July 2019
Published 15 August 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 6549—6554
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S205674
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Shreya Arora
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Jianmin Xu
Objective: Anlotinib is an oral novel multi-target tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeting vascular endothelial growth factor receptor, fibroblast growth factor receptor, platelet-derived growth factor receptor, and stem cell factor receptor (c-Kit). The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of anlotinib treatment in advanced lung cancer in the real world.
Methods: We evaluated the efficacy and toxicity of apatinib in patients with previously treated advanced lung cancer from 2018 to 2019 in Zhejiang Cancer Hospital. Survival analysis was performed by the Kaplan–Meier method.
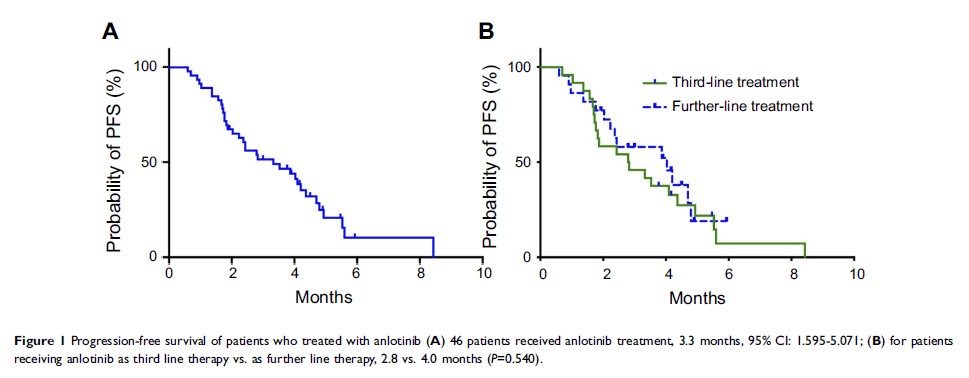
Results: Fifty-eight patients were included in the present study. Thirty-one of these patients received anlotinib treatment as a third line and 27 patients received further therapy. All 58 patients had therapeutic evaluation and 46 patients acquired progression-free survival evaluation. Ten patients achieved partial response (PR), and 36 achieved stable disease (SD), representing a response rate of 17.2% and a disease control rate of 77.6%. Median progression-free survival was 3.3 months (95% CI 1.595–5.071). The toxicities associated with anlotinib were generally acceptable with a total grade 3/4 toxicity of 5.2%. The toxicities of anlotinib were generally tolerated and the common toxicities were hand–foot syndrome and hypertension.
Conclusion: In the third-line or more-line treatment of advanced lung cancer, anlotinib appears to have some activity when utilized as a salvage treatment. Adverse reactions are controllable.
Keywords: lung cancer, anlotinib, VEGF, efficacy, safety