108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

骨骼肌质量与内脏脂肪面积比率是 2 型糖尿病和代谢综合征的重要决定因素
Authors Wang Q, Zheng D, Liu J, Fang L, Li Q
Received 9 April 2019
Accepted for publication 25 July 2019
Published 14 August 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 1399—1407
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S211529
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Melinda Thomas
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Konstantinos Tziomalos
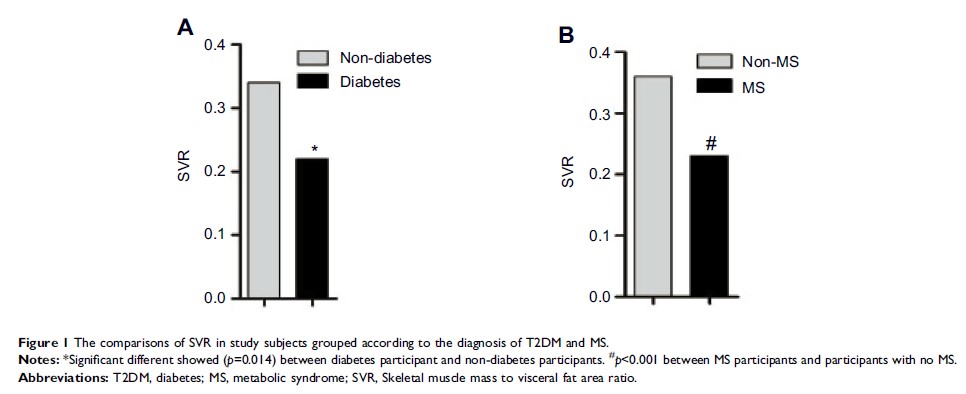
Background: Skeletal muscle mass to visceral fat area ratio (SVR) were shown to be related to some chronic diseases, such as non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases. The aim of this study is to determine whether the SVR is associated with metabolic syndrome (MS) and type 2 diabetes (T2DM).
Methods: A total of 798 subjects were included in this cross-sectional study. Lipid profiles, plasma glucose, blood pressure, waist circumference (WC) and body mass index (BMI) were grouped by the SVR. The associations between the SVR and T2DM and MS were examined using logistic regression to determine whether the SVR was associated with T2DM and MS.
Results: Lipid profiles, glucose levels, blood pressure, WC and BMI showed significant differences when stratified based on the extent of SVR. The SVR levels were also significantly higher in subjects without MS or T2DM than in those with MS or T2DM. The SVR was inversely correlated with lipid profiles and WC and was especially correlated with BMI, with an r>0.5. The SVR was identified as a risk factor for T2DM and MS after adjusting age and sex. SVR can predict T2DM [area under the curve =0.726, 95% CI (0.669–0.782), p <0.001] and MS [area under the curve =0.730, 95% CI (0.694–0.766), p <0.001]. The suitable cut-off value is 0.230 for T2DM (sensitivity 0.696, specificity 0.694) and 0.278 for the onset of MS (sensitivity 0.518, specificity 0.862).
Conclusion: The SVR is closely associated with an increased risk for exacerbating T2DM and MS and can be used as a diagnostic indicator for T2DM and MS.
Keywords: metabolic syndrome, diabetes mellitus, skeletal muscle mass, visceral fat area