109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-20b 的过度表达可预示胃癌的预后较差
Authors Xue TM, Tao LD, Zhang M, Xu GC, Zhang J, Zhang PJ
Published Date July 2015 Volume 2015:8 Pages 1871—1876
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S85236
Received 22 March 2015, Accepted 5 May 2015, Published 24 July 2015
Approved for publication by Professor Daniele Santini
Background: miR-20b has been shown to be aberrantly expressed in several tumor types. However, the clinical significance of miR-20b in the prognosis of patients with gastric cancer (GC) is poorly understood, and the exact role of miR-20b in GC remains unclear.
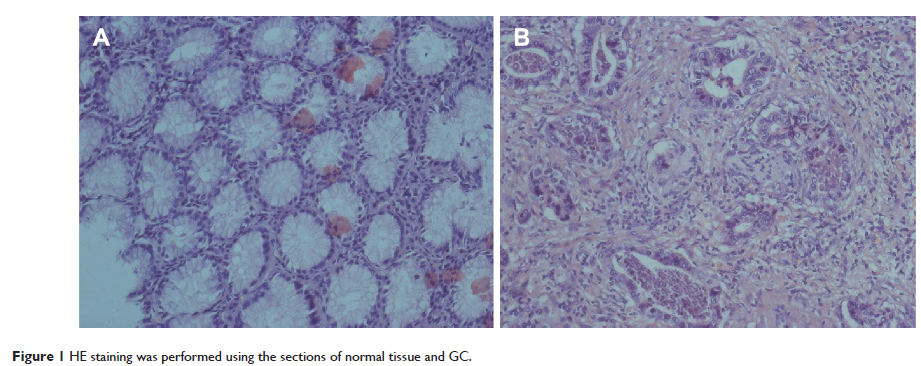
Materials and methods: The expression of miR-20b was detected in 102 patients with GC by a SYBR Green assay and was compared with the expression in matched adjacent normal tissue specimens. The aim of the present study was to investigate the association of the expression of miR-20b with the clinicopathological characteristics and the overall survival of patients with GC as analyzed by Kaplan–Meier analysis and Cox proportional hazards regression models.
Results: Our results showed that miR-20b expression was upregulated in GC tissue compared with normal mucosa (P =0.00). Furthermore, miR-20b expression was positively correlated with advanced lymph node metastasis (P =0.041), tumor node metastasis stage (P =0.000), and deeper and distant metastasis (P =0.031). The overall survival rate of patients with GC was significantly lower in those whose tumors expressed high levels of miR-20b mRNA compared with those whose tumors expressed low levels of miR-20b mRNA (P =0.019).
Conclusion: miR-20b may serve as a potential molecular marker for the prognosis of GC.
Keywords: miR-20b, microRNA, cancer, clinicopathology