108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

缺氧诱导因子 1αmRNA 表达的上调与肝细胞癌患者预后不良有关
Authors Cheng W, Cheng Z, Yang Z, Xing D, Zhang M
Received 5 December 2018
Accepted for publication 21 July 2019
Published 9 August 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 6285—6296
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S197077
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Jianmin Xu
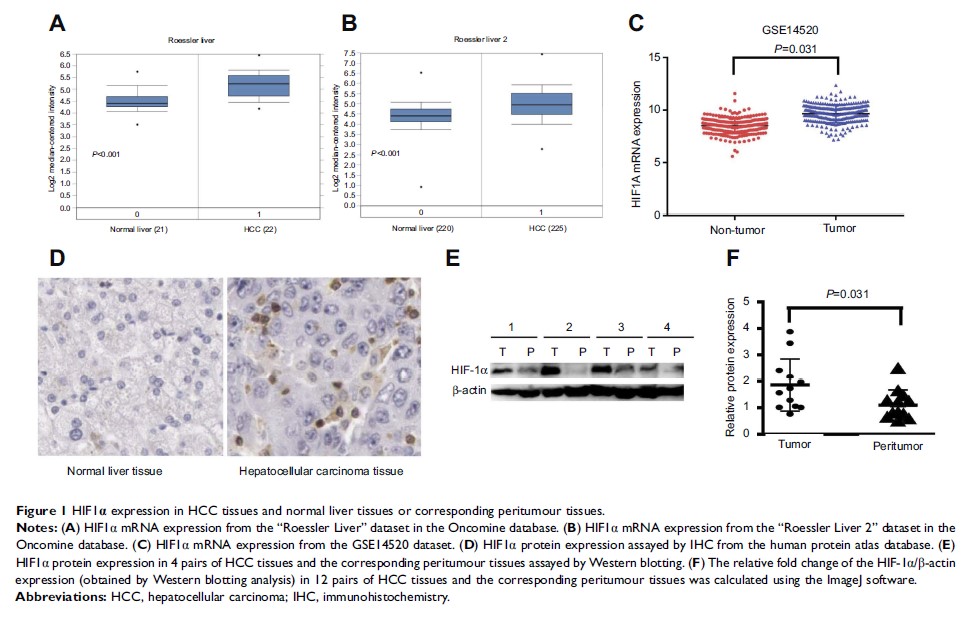
Background: HIF1α mRNA expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissues and its relationship with the prognosis in HCC patients is still unclear. We performed this study to investigate the expression of HIF1α mRNA and its correlation with the prognosis in HCC patients.
Materials and methods: GSE14520 and Oncomine database were used to analyse the differential expression of HIF1α mRNA among HCC tissues and corresponding peritumour tissues or normal liver tissues. The relationship between HIF1α mRNA expression and the clinicopathological features and survival in HCC patients was analysed using the GSE14520 dataset. CCK-8 assay, wound-healing assay, transwell invasion assay, tube formation assay, and subcutaneous xenograft tumour assays using nude mice were used to confirm the function of HIF1α.
Results: Expression of HIF1α mRNA was significantly upregulated in HCC tissues (P <0.05 in all cases); this was supported by the results of the Western blotting (P =0.031) and IHC analyses. Our analysis of the clinicopathological features of HCC patients indicated that high HIF1α mRNA expression was strongly related with TNM stage III (P =0.002) and BCLC stage C (P =0.038). Survival analysis demonstrated that HCC patients with high HIF1α mRNA expression had a short overall survival (OS) (P =0.048), but showed no significant difference in recurrence-free survival (RFS) (P =0.066) compared to patients with low HIF1α mRNA expression. We further demonstrated that HIF1α promoted the proliferation, migration, invasion, and angiogenic ability of HCC cells, by using the stably transformed SK-Hep1 and Hep-3B cell lines showing HIF1α overexpression. Finally, xenograft tumour models of nude mice showed that RNA interference-mediated HIF1α silencing suppressed tumour growth and angiogenesis in HCC.
Conclusion: Our study suggests that the upregulation of HIF1α mRNA, which is found in HCC tissues and associated with poor prognosis in HCC patients, contributed to the proliferation, migration, invasion, and angiogenic ability of HCC cells.
Keywords: HIF1α, mRNA, prognosis, hepatocellular carcinoma