108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过白蛋白剥离制备的二硫化钛纳米片:用于光热/放射协同疗法治疗结肠癌的多功能纳米平台
Authors Cao C, Zhang J, Yang C, Xiang L, Liu W
Received 30 March 2019
Accepted for publication 21 June 2019
Published 9 August 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 6337—6347
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S210618
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Aruna Narula
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
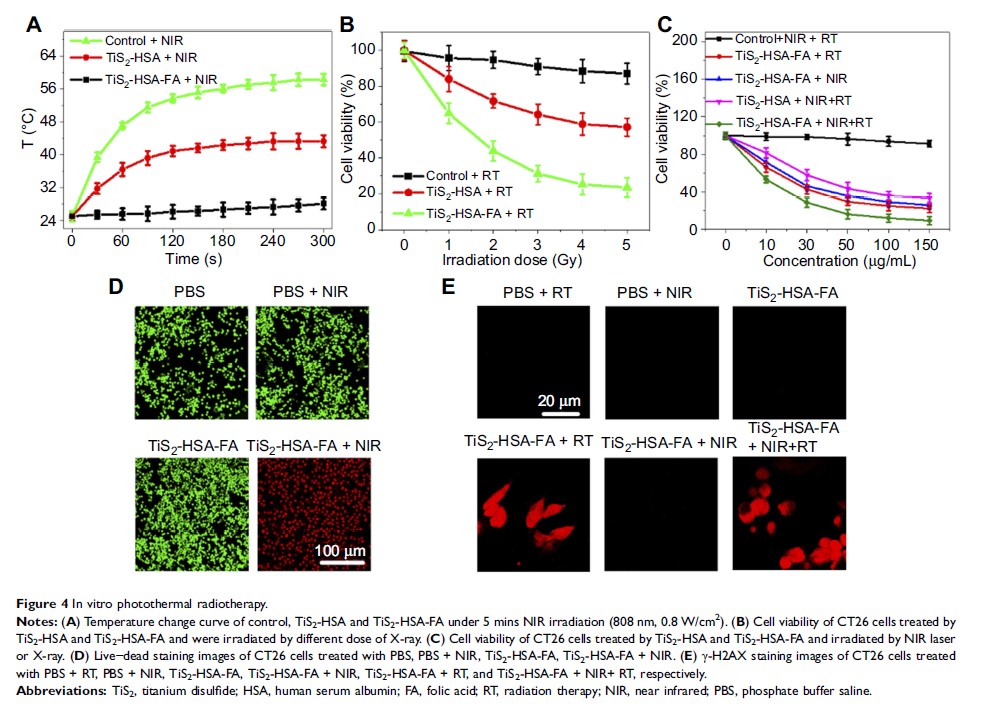
Purpose: TiS2-HSA-FA, a nanoagent based on titanium disulfide (TiS2), human serum albumin (HSA), and folic acid (FA), was synthesized for potential use in synergistic photothermal/radiation therapy for colon cancer.
Methods: TiS2 nanosheets were synthesized through a HSA-assisted exfoliation method and then modified with PEGylated FA. The morphology, size, zeta potential, stability, cellular uptake, cytotoxicity, biodistribution, and in vitro and in vivo biocompatibility of the nanoparticles as well as their suitability for synergistic photothermal/radiation colon cancer therapy were investigated.
Results: The as-synthesized TiS2-HSA-FA nanoparticles showed excellent physiological stability, as well as high absorption values in the near-infrared (NIR) and X-ray regions, giving them superb activity as a photothermal and radiation sensitizer. In vitro and in vivo experiments indicated that TiS2-HSA-FA showed high tumor targeting selectivity, blood circulation time, biocompatibility, and suitability for synergistic tumor photothermal radiotherapy.
Conclusion: A multifunctional nanoplatform based on TiS2 was developed and found to be potentially suitable for synergistic photothermal/radiation therapy for colon cancer.
Keywords: titanium disulfide, tumor target, photothermal therapy, radiotherapy, synergistic colon cancer therapy