108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miRNA-499 rs3746444 A>G 变异与食管胃结合部腺癌(AEG)风险及淋巴结状态的关系
Authors Tang W, Wang Y, Pan H, Qiu H, Chen S
Received 17 March 2019
Accepted for publication 11 July 2019
Published 8 August 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 6245—6252
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S209013
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Rachel Predeepa
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjay Singh
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) miRNA-499 rs3746444 A>G polymorphism may be complicated in the susceptibility to cancer. However, the correlation of this polymorphism with adenocarcinoma of esophagogastric junction (AEG) was unknown.
Patients and methods: A total of 1063 AEG patients and 1677 controls were included in this study to assess the association of miR-499 rs3746444 A>G with AEG risk. SNPscanTM genotyping assay was harnessed to obtain the genotypes of miRNA-499 rs3746444 A>G polymorphism.
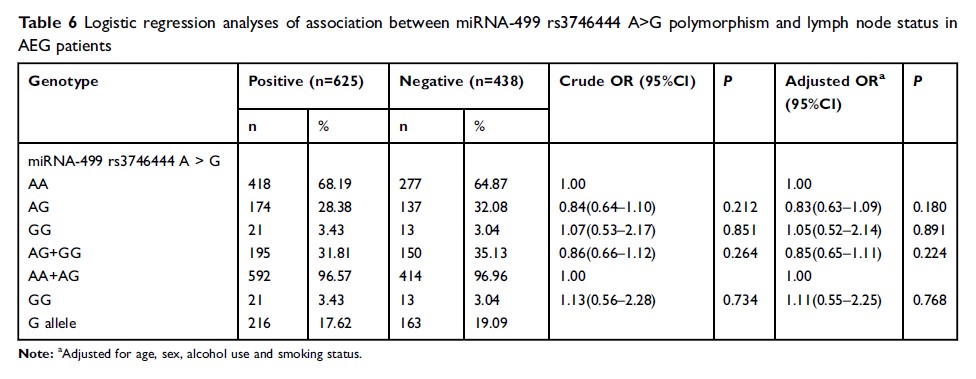
Results: We identified that SNP miR-499 rs3746444 A>G increased the susceptibility of AEG (AG vs AA: adjusted OR=1.25, 95% CI=1.05–1.49, P =0.012 and AG/GG vs AA: adjusted OR=1.30, 95% CI=1.10–1.54, P =0.002). In a stratified analysis, we found that miR-499 rs3746444 A>G polymorphism had an increased susceptibility of AEG in several subgroups (male subgroup: AG vs AA: adjusted P =0.004 and AG/GG vs AA: adjusted P =0.002; female subgroup: GG vs AG/AA: adjusted P =0.046; <64 years subgroup: AG vs AA: adjusted P =0.006 and AG/GG vs AA: adjusted P =0.003; never smoking subgroup: AG vs AA: adjusted P =0.003 and AG/GG vs AA: adjusted P =0.001; and never drinking subgroup: AG vs AA: adjusted P =0.008 and AG/GG vs AA: adjusted P =0.002). The results of power calculation indicated that miR-499 rs3746444 A>G polymorphism increased the risk of AEG in overall comparison, male, <64 years, never smoking, and never drinking subgroups. Among the AEG cases, 625 patients accompanied by positive lymph node. However, the distribution of miRNA-499 rs3746444 A>G variants was no significant difference between different lymph node status.
Conclusion: Our findings indicate that miR-499 rs3746444 A>G polymorphism is significantly associated with AEG susceptibility. In the future, further exploration of this genetic factor in relation to AEG susceptibility with an adequate methodological quality is needed.
Keywords: miRNA-499, polymorphism, susceptibility, lymph node metastasis, adenocarcinoma of esophagogastric junction