108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

社区获得性肺脓肿可归因于牙源性菌群
Authors Guo W, Gao B, Li L, Gai W, Yang J, Zhang Y, Wang L
Received 10 June 2019
Accepted for publication 16 July 2019
Published 8 August 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 2467—2470
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S218921
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Suresh Antony
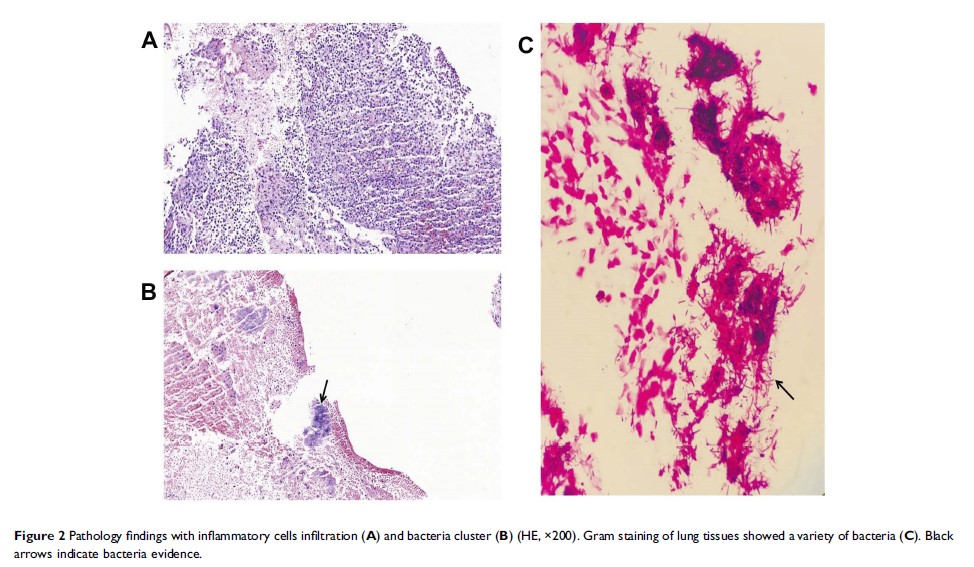
Abstract: A lung abscess is an infectious pulmonary disease characterized by pus-filled cavity formation and often an air-fluid level. In this article, we described an indolent community-acquired lung abscess suspected as a tumor previously. A 56-year-old male presented with cough and expectoration for 2 months and hemoptysis for 2 weeks. His physical examinations, whole blood count and C-reactive protein level were normal. The chest computed tomography (CT) scan showed a 40×38×39 mm high-density mass in the right upper pulmonary lobe, with irregular borders. The pathology of a CT-guided percutaneous needle aspiration biopsy showed numerous inflammatory cells and bacteria infiltration without tumor lesions. Bacteriological detection of lung tissue revealed the cause was odontogenic flora. A next-generation sequencing demonstrated the etiologic correlation between lung abscess and periodontitis. After a 2-month pathogen-directed oral antibiotics therapy combined with chlorhexidine gargle oral care, this patient showed a remarkable improvement. Periodontitis can be a cause of a lung abscess, which would be taken into account in the treatment regimes preventing infectious recurrence.
Keywords: community-acquired lung abscess, periodontitis, odontogenic flora