108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

全身牛磺酸治疗提供针对视网膜光感受器变性和视功能损伤的神经保护作用
Authors Tao Y, He M, Yang Q, Ma Z, Qu Y, Chen W, Peng G, Teng D
Received 11 November 2018
Accepted for publication 1 May 2019
Published 7 August 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 2689—2702
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S194169
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tuo Deng
Objective: Retinitis pigmentosa causes progressive photoreceptor degeneration in the subjects while no clinical therapy exists. The present study sought to evaluate the potential protective effects of taurine on a pharmacologically induced RP animal model.
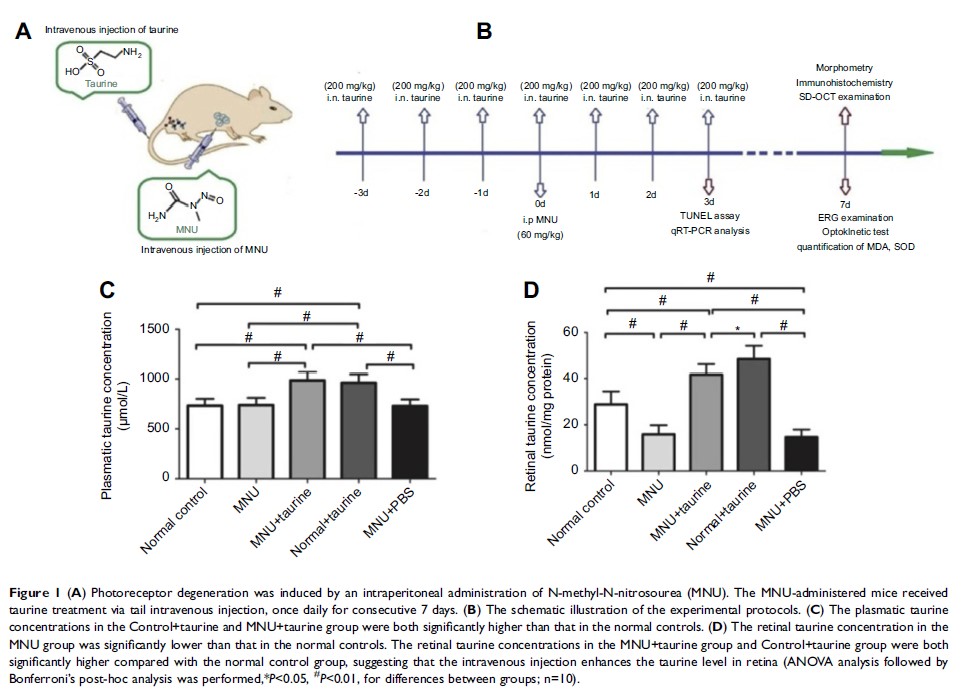
Methods: Photoreceptor degeneration in mice was induced by an intraperitoneal injection of N-methyl-N-nitrosourea (MNU). The MNU-administrated mouse received taurine treatment and then they were examined by electroretinography, spectral-domain optical coherence tomography, optokinetic test, and histological and immunohistochemistry assay.
Results: Prominent taurine deficiency was found in the retinas of MNU-administered mice. Intravenous taurine treatment increased significantly the retinal taurine level. Morphological studies showed that taurine could alleviate the retinal disorganizations in the MNU-induced mice. Taurine also ameliorated the visual impairments in the MNU-induced mice as evidenced by functional examinations. Immunostaining experiments demonstrated that both the M-cone and S-cone populations in the degenerative retinas are rescued by taurine. In particular, the M-cone photoreceptors in superior-temporal quadrant and the S-cone photoreceptors in inferior-nasal quadrant were preferentially rescued. Mechanism study showed that the photoreceptor apoptosis and oxidative stress in the degenerative retina were effectively alleviated by taurine treatment.
Conclusion: Taurine is protective against the MNU-induced photoreceptor degeneration. Systemic taurine administration may act as a promising therapeutic potion for retinopathies with chronic cycle.
Keywords: neural degeneration, retina, therapeutics