108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

从杨桃根分离的 2-十二烷基-6-甲氧基-2,5-二烯-1,4-环己二酮 通过抑制 TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB 通路改善糖尿病肾病
Authors Lu S, Zhang H, Wei X, Huang X, Chen L, Jiang L, Wu X, Zhou X, Qin L, Li Y, Lin X, Huang R
Received 20 March 2019
Accepted for publication 16 May 2019
Published 7 August 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 1355—1363
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S209436
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Melinda Thomas
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Konstantinos Tziomalos
Background: Averrhoa carambola L. is a traditional medicinal herb that has long been used to treat diabetes. Our previous studies found that 2-dodecyl-6-methoxycyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione (DMDD) isolated from A. carambola L. roots could ameliorate diabetic nephropathy (DN), but its exact mechanism remains unclear.
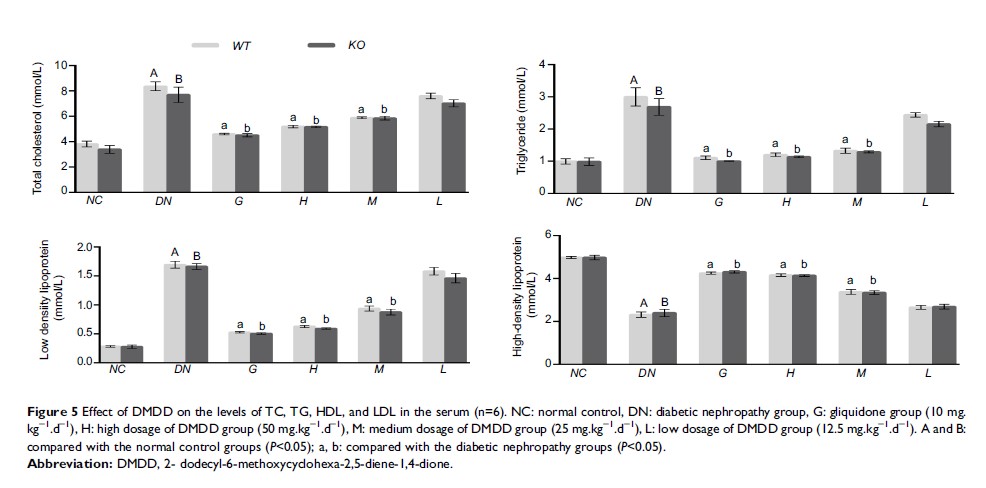
Methods: A DN model was established by streptozotocin (STZ, 100 mg/kg body weight) in TLR4 knockout (TLR4-/-, KO) mice and wild-type (WT) mice. Body weight and blood glucose were evaluated after oral administration of DMDD (12.5, 25, 50 mg/kg body weight/d) in diabetic mice. The levels of serum lipids, including TC, TG, HDL, and LDL and kidney function indexes Scr and BUN, were detected by biochemical equipment. The levels of inflammatory cytokines including IL-6 and TNF-α, were determined by ELISA kits. Furthermore, changes in renal ultrastructure were observed by electron microscopy. Western blot analysis and RT-PCR were used to assess the protein expression and mRNA levels of TLR4, MyD88 and NF-κB.
Results: DMDD treatment attenuated diabetic nephropathy, as a result of a decline in blood glucose, serum creatinine, and blood urine nitrogen levels and an increase in the quantity and density of podocytes, combined with improved dyslipidaemia. DMDD treatment inhibited the inflammatory response and downregulated the expression of the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway in diabetic mice, and these changes were significantly different in TLR4-/- mice.
Conclusion: DMDD alleviates diabetic nephropathy by mitigating kidney damage and inflammation via the inhibition of the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signalling pathway.
Keywords: 2-dodecyl-6-methoxycyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione, diabetic nephropathy, TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signalling pathway