108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miRNA-15a 通过调节 AKT 通路来调节甲状腺乳头状癌的增殖和凋亡
Authors Jin J, Zhang J, Xue Y, Luo L, Wang S, Tian H
Received 23 April 2019
Accepted for publication 23 June 2019
Published 6 August 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 6217—6226
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S213210
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Aruna Narula
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Gaetano Romano
Aim: Aberrantly expressed microRNAs (miRNAs) are involved in many diseases including cancer. The expression of miR-15a was reported to be downregulated in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) compared to control tissue. However, the mechanism underlying this downregulation remains unclear.
Methods: The effects of miR-15a on the proliferation and invasion of PTC cells were evaluated by CCK-8 and transwell assays, respectively. Expression levels of AKT and rearranged during transfection (RET) in cells were assessed using Western blotting. The correlation of RET and miR-15a was validated by luciferase reporter assay. Moreover, in vivo assay was performed to demonstrate the effect of miR-15a on tumor growth.
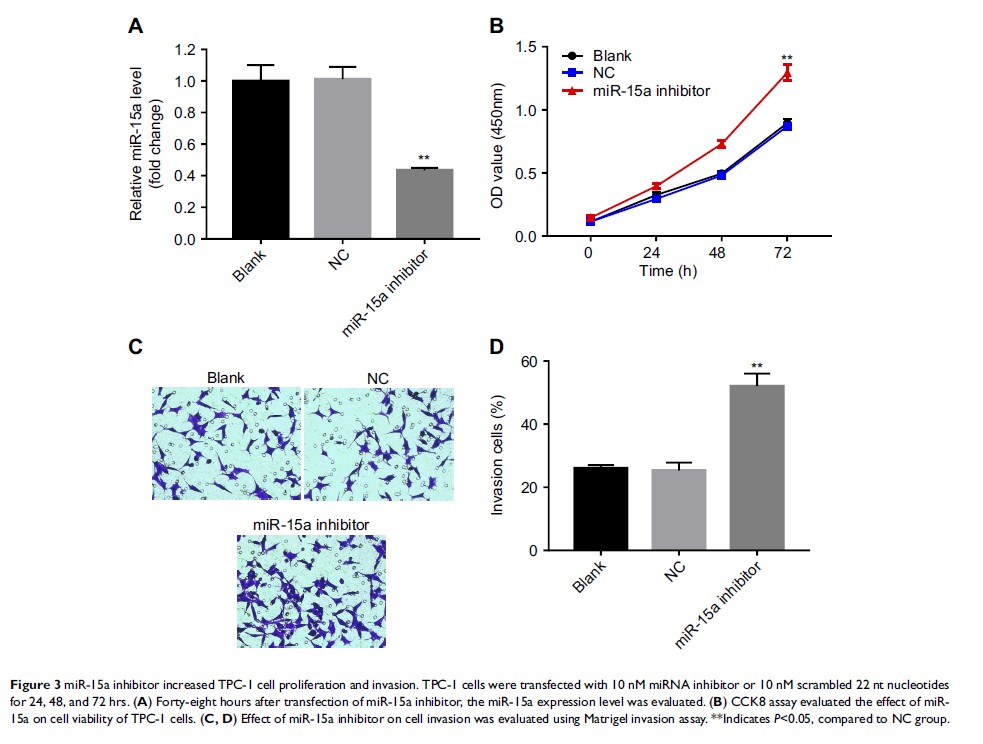
Results: We confirmed that the expression of miR-15a was significantly lower in PTC tissue than that in normal tissue. Overexpression of miR-15a notably inhibited PTC cell proliferation and invasion via promoting apoptosis. Additionally, RET was found to be a target of miR-15a and this correlation was confirmed by dual-luciferase assay and Western blot. Furthermore, in vivo study revealed that overexpression of miR-15a inhibited tumor growth via downregulating the levels of RET and phosphorylated AKT.
Conclusion: In the present study, we demonstrated that miR-15a played an antitumor role in regulating PTC via targeting RET/AKT pathway. Therefore, miR-15a may serve as a potential molecular target for the treatment of PTC.
Keywords: miRNA-15a, papillary thyroid carcinoma, AKT pathway, apoptosis