108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

免疫应答相关基因模块与头颈部鳞状细胞癌临床特征的相关性
Authors Song Y, Pan Y, Liu J
Received 13 January 2019
Accepted for publication 17 July 2019
Published 6 August 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 7455—7472
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S201177
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
Purpose: Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is the sixth most prevalent cancer in the world, accounting for more than 90% of head and neck malignant tumors. However, its molecular mechanism is largely unknown. To help elucidate the potential mechanism of HNSCC tumorigenesis, we investigated the gene interaction patterns associated with tumorigenesis.
Methods: Weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) can help us to predict the intrinsic relationship or correlation between gene expression. Additionally, we further explored the combination of clinical information and module construction.
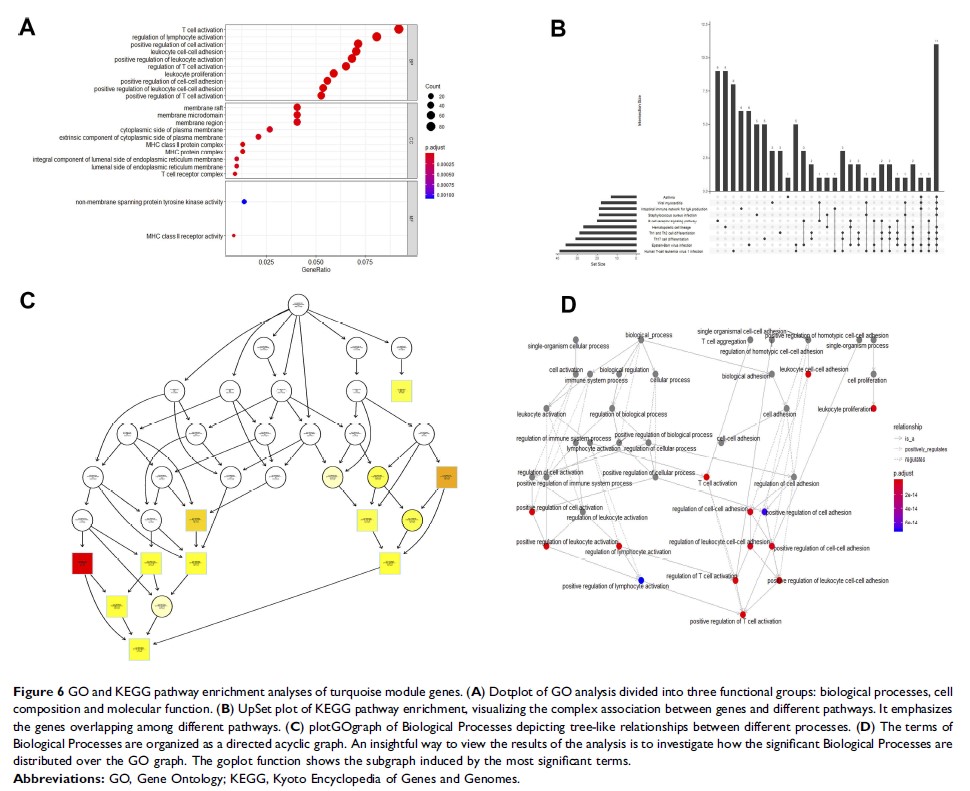
Results: Sixteen modules were constructed, among which the key module most closely associated with clinical information was identified. By analyzing the genes in this module, we found that the latter may be related to the immune response, inflammatory response and formation of the tumor microenvironment. Sixteen hub genes were identified—ARHGAP9 , SASH3 , CORO1A , ITGAL , PPP1R16B ,TBC1D10C , IL10RA , ITK , AKNA , PRKCB , TRAF3ip3 , GIMAP4 , CCR7 , P2RY8 , GIMAP7 , and SP140 . We further validated these genes at the transcriptional and translation levels.
Conclusion: The innovative use of a weighted network to analyze HNSCC samples provides new insights into the molecular mechanism and prognosis of HNSCC. Additionally, the hub genes we identified can be used as biomarkers and therapeutic targets of HNSCC, laying the foundation for the accurate diagnosis and treatment of HNSCC in clinical and research in the future.
Keywords: head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, wgcna, co-expression, gene module, hub gene, immune response-related genes