108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

c.415C> T,c.52G> A 和 NUDT15 的 36_37insGGAGTC 多态性与硫嘌呤诱导的白细胞减少、硫嘌呤不耐受和严重脱发之间的关联:更新的荟萃分析
Authors Wang R, Liu B, Li J, Xu J, Wang X, Zhao Z, Zhao L
Received 29 March 2019
Accepted for publication 1 July 2019
Published 5 August 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 2729—2744
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S210512
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Qiongyu Guo
Purpose: As a common immunosuppressive and anticancer drug, thiopurine has achieved remarkable clinical success. However, higher inter-individual dose variability and unpredictable toxicity still challenge its use in clinical practices. Some studies indicate that NUDT 15 polymorphisms are associated with this variation, but specific correlation remains controversial. This meta-analysis assessed the association between three polymorphisms of NUDT 15 and thiopurine-induced toxicities.
Methods: Three databases were electronically searched: PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science. Only case–control studies and cohort studies were eligible. The overall pooled ORs and corresponding 95% CIs were used to represent the results.
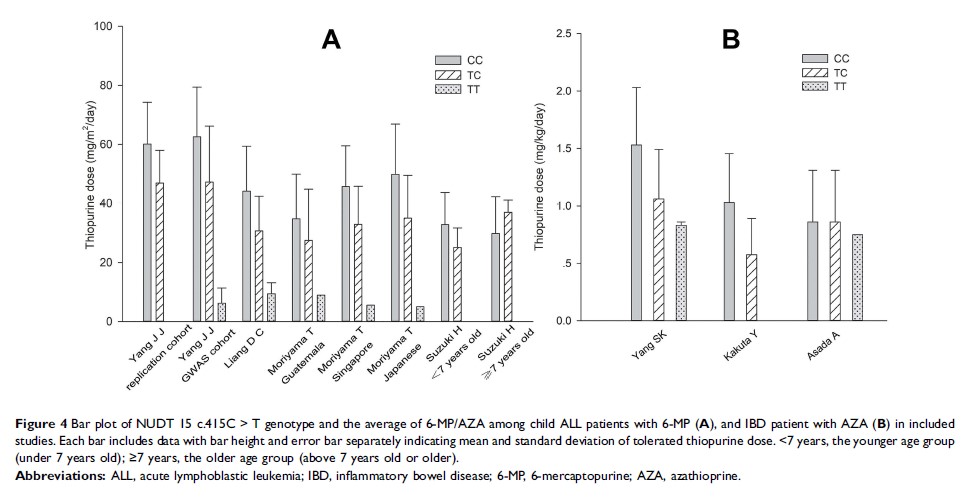
Findings: We included 16 studies that focus on NUDT 15 c.415C > T, c.52G > A, and 36_37insGGAGTC polymorphisms in patients treated with thiopurine. Significant associations between NUDT 15 c.415C > T polymorphism and leukopenia were found in all genetic models (TC/TT vs CC, OR: 7.64, 95% CI: (6.19, 9.44), P <0.00001; TT vs CC/TC, OR: 29.66, 95% CI: (12.31, 71.46), P <0.00001; TT vs CC, OR: 45.60, 95% CI: (18.84, 110.37), P <0.00001; TC vs CC, OR: 6.41, 95% CI: (5.19, 7.94), P <0.00001; TT vs TC, OR: 6.38, 95% CI: (2.59, 15.72), P <0.00001), early/late leukopenia (in recessive and co-dominant model), leukopenia (grade 3–4), and severe hair loss in all genetic models. Besides, c.52G > A and 36_37insGGAGTC polymorphisms were also significantly associated with leukopenia. No significant association between NUDT 15 c.415C > T polymorphism and early/late leukopenia in the Chinese population was determined in the co-dominant model (TC vs CC).
Implications: NUDT 15 c.415C > T polymorphism could increase the risk of leukopenia, early/late leukopenia, leukopenia (grade 3–4), and severe hair loss. Meanwhile, c.52G > A and c.36_37insGGAGTC mutations also probably increase the risk of leukopenia. Preemptive tests for NUDT 15 polymorphisms are highly recommended to individualize the treatment of thiopurine for a better outcome with less toxicity.
Keywords: NUDT 15, polymorphism, leukopenia, thiopurine, intolerance, meta-analysis