108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

用聚精氨酸肽修饰的纳米结构脂质载体凝胶改善氯诺昔康经皮给药以治疗角叉菜胶诱导的大鼠足爪水肿
Authors Gao S, Tian B, Han J, Zhang J, Shi Y, Lv Q, Li K
Received 14 February 2019
Accepted for publication 12 June 2019
Published 2 August 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 6135—6150
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S205295
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Thiruganesh Ramasamy
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Background: Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) are emerging as attractive drug carriers in transdermal drug delivery. The surface modification of NLCs with cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) can enhance the skin permeation of drugs.
Purpose: The objective of the current study was to evaluate the ability of the cell-penetrating peptide (CPP) polyarginine to translocate NLCs loaded with lornoxicam (LN) into the skin layers and to evaluate its anti-inflammatory effect.
Methods: The NLCs were prepared using an emulsion evaporation and low temperature solidification technique using glyceryl monostearates, triglycerides, DOGS-NTA-Ni lipids and surfactants, and then six histidine-tagged polyarginine containing 11 arginine (R11) peptides was modified on the surface of NLCs.
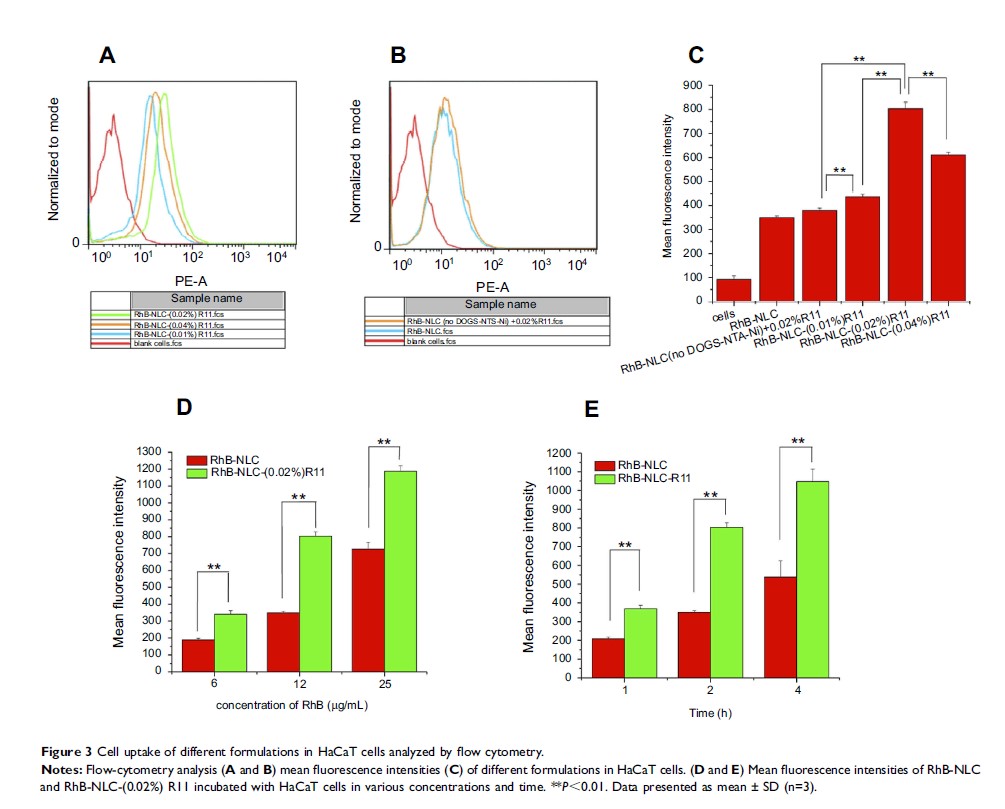
Results: The developed NLCs formulated with LN and R11 (LN-NLC-R11) were incorporated into 2% HPMC gels. NLCs were prepared with a particle size of (121.81±3.61)–(145.72±4.78) nm, and the zeta potential decreased from (−30.30±2.07) to (−14.66±0.74) mV after the modification of R11 peptides. The encapsulation efficiency and drug loading were (74.61±1.13) % and (7.92±0.33) %, respectively, regardless of the surface modification. Cellular uptake assays using HaCaT cells suggested that the NLC modified with R11 (0.02%, w/w) significantly enhanced the cell internalization of nanoparticles relative to unmodified NLCs (P <0.05 or P <0.01). An in vitro skin permeation study showed better permeation-enhancing ability of R11 (0.02%, w/w) than that of other content (0.01% or 0.04%). In carrageenan-induced rat paw edema models, LN-NLC-R11 gels inhibited rat paw edema and the production of inflammatory cytokines compared with LN-NLC gels and LN gels (P <0.01).
Conclusion: In our investigation, it was strongly demonstrated that the surface modification of NLC with R11 enhanced the translocation of LN across the skin, thereby alleviating inflammation.
Keywords: lornoxicam, nanostructured lipid carriers, cell penetrating peptides, transdermal drug delivery, anti-inflammatory effect