108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

小分子抑制剂 MCC950 通过抑制 NLRP3 炎症小体激活改善糖尿病肾病中的肾损伤
Authors Zhang C, Zhu X, Li L, Ma T, Shi M, Yang Y, Fan Q
Received 28 December 2018
Accepted for publication 24 May 2019
Published 2 August 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 1297—1309
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S199802
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 6
Editor who approved publication: Dr Steven F. Abcouwer
Background: Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is a lethal diabetic microvascular complication characterized by chronic low-grade inflammation. The NOD-like receptor pyrin domain-containing protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome is implicated in the progression of DN. MCC950 is a selective and potent inhibitor of NLRP3; however, its efficacy in DN requires further investigation.
Methods: To investigate the efficacy of MCC950 in DN, eight-week-old type 2 diabetic db/db mice received injections of MCC950 intraperitoneally (10 mg/kg) twice per week for 12 weeks. Urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (ACR) and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL), renal function, pathological changes, markers of podocyte and fibrosis and NLPR3/caspase-1/IL-1β expression in the renal cortices of db/db mice were evaluated. High-glucose (HG)-treated rat glomerular mesangial cells were treated with various concentrations of MCC950 for 48 hrs. Markers of fibrosis and NLPR3/caspase-1/IL-1β expression in the glomerular mesangial cells were measured.
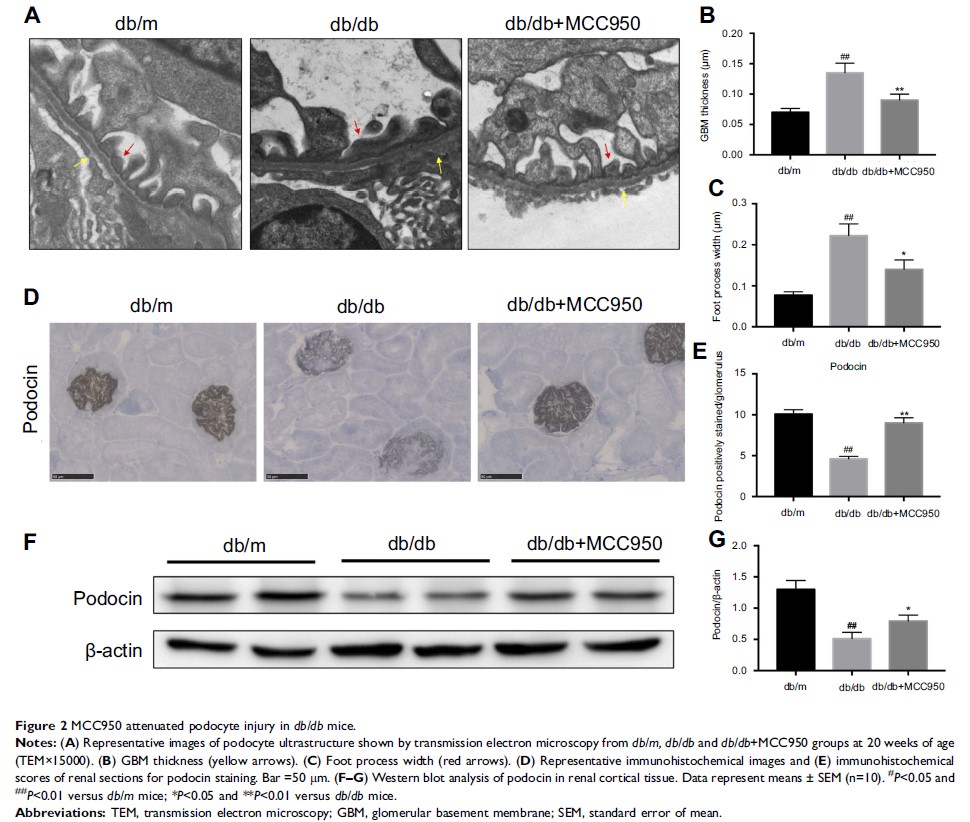
Results: The NLRP3 inflammasome was activated in db/db mice and HG-induced mesangial cells by upregulating NLRP3/caspase-1/IL-1β pathway. Inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome with MCC950 reduced the production of active caspase-1 and active IL-1β in db/db mice and HG-induced mesangial cells. MCC950 reduced serum creatinine, urinary ACR and NGAL, attenuated mesangial expansion with increased matrix and tubular dilatation, alleviated thickened glomerular basement membrane (GBM) and foot process fusion without affecting body weight and blood glucose levels in db/db mice. MCC950 increased the expression of podocin in db/db mice, and decreased the expression of TGF-β1, fibronectin, collagen I and α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) in renal cortices of db/db mice and HG-induced mesangial cells.
Conclusion: MCC950 ameliorated renal function, thickened GBM, podocyte injury and renal fibrosis in db/db mice, and decreased the production of fibrosis markers in HG-induced mesangial cells. MCC950 effectively ameliorated diabetic kidney injury by inhibiting NLRP3/caspase-1/IL-1β pathway, which may be a potential therapeutic strategy to prevent the progression of DN.
Keywords: diabetic nephropathy, MCC950, NLRP3 inflammasome, db/db mice, mesangial cells