108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

IRF2BP2-RARA 融合的急性早幼粒细胞白血病罕见病例;及文献评论
Authors Liu Y, Xu F, Hu H, Wen J, Su J, Zhou Q, Qu W
Received 29 May 2019
Accepted for publication 11 July 2019
Published 2 August 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 6157—6163
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S217622
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Shreya Arora
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
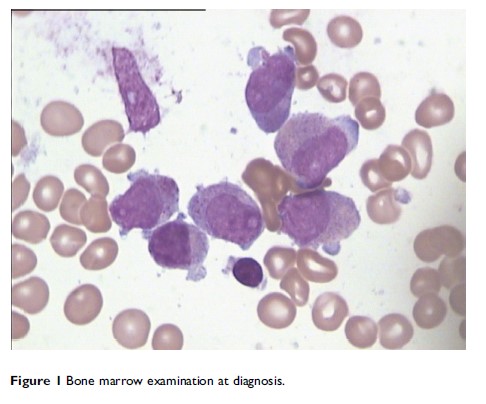
Background: Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) is commonly characterized by the fusion of retinoic acid receptor alpha (RARA) with promyelocytic leukemia (PML). Most APL patients acquire long-term survival after treatment with all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) or arsenic agents-based chemotherapy.
Case presentation: A rare case of APL was reported after IRF2BP2-RARA was detected in the relapsed process using next-generation RNA-sequencing analysis. In addition, the mutation of NRAS was also detected. ATRA and arsenic trioxide combined with daunorubicin were used during induction treatment. The patient acquired complete remission but relapsed in 12 months. The patient was resistant to all other chemotherapies and refused any further therapy. The literature review indicated that allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation might be a therapeutic method to treat APL with IRF2BP2-RARA fusion.
Conclusion: Atypical APL should be considered even if the patients present with normal chromosomal karyotype and no classic PML-RARA fusions, but classical clinical features and bone marrow cell morphology. We reported a case of APL with IRF2BP2-RARA fusion was shown to harbor the NRAS mutation at relapse.
Keywords: acute promyelocytic leukemia, IRF2BP2-RARA, variant translocation, gene fusion, NRAS, mutation