108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长非编码 RNA SNHG16 沉默通过上调 microRNA-628-3p 抑制胃癌的侵袭性,从而减少 NRP1
Authors Pang W, Zhai M, Wang Y, Li Z
Received 18 April 2019
Accepted for publication 5 July 2019
Published 1 August 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 7263—7277
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S211856
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Kenan Onel
Background: MicroRNA-628-3p (miR-628) has been reported to play important roles in the progression of multiple human cancer types. Nonetheless, whether the expression profile of miR-628 is altered in gastric cancer remains unclear and whether its aberrant expression plays a crucial part in the aggressiveness of gastric cancer is yet to be determined. Therefore, in this study, we systematically investigated the involvement of miR-628 in gastric cancer progression.
Materials and methods: MiR-628 expression in gastric cancer tissues and cell lines were determined via reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). A CCK-8 assay, flow-cytometric analysis, Transwell assays, and a xenograft model experiment were performed to evaluate the influence of miR-628 overexpression on gastric cancer cells. Notably, the mechanisms underlying the tumor-suppressive activity of miR-628 in gastric cancer cells were explored by bioinformatics analysis, a luciferase reporter assay, RT-qPCR, and Western blotting.
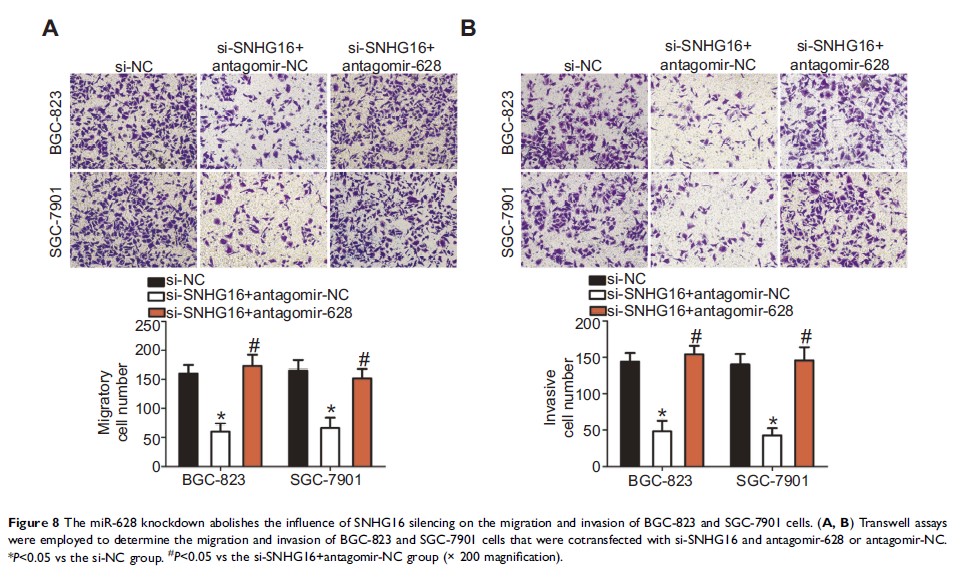
Results: MiR-628 expression was low in gastric cancer tissue samples and cell lines. The low expression of miR-628 was closely associated with the lymph node metastasis, invasive depth and TNM stage among patients with gastric cancer. Further clinical analysis indicated that patients with gastric cancer underexpressing miR-628 had a worse prognosis than did the patients with high miR-628 expression in the tumor. Overexpressed miR-628 restrained proliferation, migration, and invasion; induced apoptosis; and impaired tumor growth of gastric cancer cells. In addition, neuropilin 1 (NRP1) mRNA was validated as the direct target of miR-628 in gastric cancer. Long noncoding RNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 16 (SNHG16) was demonstrated to sponge miR-628 in gastric cancer. Moreover, miR-628 knockdown abrogated the influence of SNHG16 silencing on gastric cancer cells.
Conclusion: Our findings elucidate how the SNHG16–miR-628–NRP1 pathway serves as a regulatory network playing crucial roles in gastric cancer progression, suggesting that this pathway may be a novel target of anticancer therapy.
Keywords: gastric cancer, microRNA-628-3p, long noncoding RNA, neuropilin 1, small nucleolar RNA host gene 16