108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

用于计算机断层扫描实时成像和胃滞留药物输送的儿茶酚接枝的壳聚糖海藻酸盐/硫酸钡微胶囊的构建
Authors Du F, Wu Y, Du F, Zhang L, Feng W, Zhao L, Cai R, Xu L, Bian G, Li J, Zou S, Gong A, Zhang M
Received 5 February 2019
Accepted for publication 23 April 2019
Published 31 July 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 6001—6018
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S204237
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
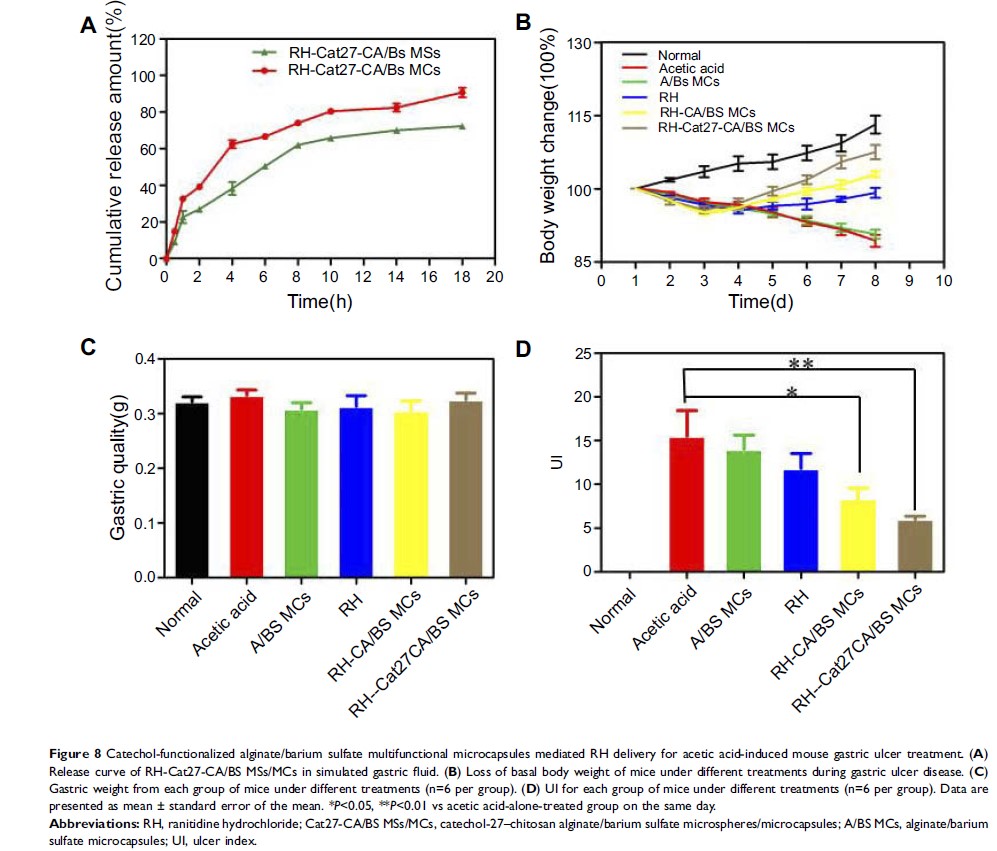
Background: The gastroretentive drug delivery system is an effective administration route, which can improve the bioavailability of the drug and the therapeutic effect by prolonging the release time of the drug and controlling the release rate in the stomach.
Methods: Inspired by the excellent adhesion properties of mussel protein, we prepared novel catechol-grafted chitosan alginate/barium sulfate microcapsules (Cat-CA/BS MCs) with mucoadhesive properties and computed tomography (CT) imaging function for gastric drug delivery. First, barium sulfate nanoclusters used as CT contrast agent were synthesized in situ in the Cat-CA/BS MCs through a one-step electronic spinning method. Next, catechol-grafted chitosan as the mucoadhesive moiety was coated on the surface of Cat-CA/BS MCs by polyelectrolyte molecule self-assembly.
Results: The prepared Cat-CA/BS MCs could effectively retained in the stomach for 48 hours and successively released ranitidine hydrochloride, which could be used for the treatment of gastric ulcer. Cat-CA/BS MCs exhibited superior CT contrast imaging properties for real-time tracking in vivo after oral administration.
Conclusion: These findings demonstrate that Cat-CA/BS MCs serving as multifunctional oral drug carriers possess huge potential in gastroretentive drug delivery and non-invasive visualization.
Keywords: catechol, mucoadhesive, microcapsules, CT imaging, gastroretentive drug delivery