108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

lncRNA FOXD2-AS1 通过调节 miR185-5p-SIX1 轴赋予非小细胞肺癌顺铂耐药性
Authors Ge P, Cao L, Yao YJ, Jing RJ, Wang W, Li HJ
Received 7 December 2018
Accepted for publication 29 April 2019
Published 30 July 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 6105—6117
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S197454
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leo Jen-Liang Su
Background: Chemoresistance is a major obstacle for chemotherapy failure in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). lncRNAs are a class of pivotal regulators in various cancers, and the lncRNA FOXD2-AS1 is implicated in the progression of NSCLC. However, it is still unclear whether it regulates chemosensitivity.
Methods: Expression levels of FOXD2-AS1, miR185-5p, and SIX1 mRNA were identified by reverse-transcription qPCR. CCK8 assay was performed to assess cell proliferation and chemosensitivity of cisplatin-resistant A549/DDP and H1299/DDP cells. Colony-forming assay was utilized to detect colony numbers. Cell migration and invasion ability were measured by transwell assay. The protein levels of LRP, Pgp, MRP1, and SIX1 were examined by Western blot assay. The correlation between FOXD2-AS1 and miR185-5p or miR185-5p and SIX1 were validated by bioinformatic, dual-luciferase, and RNA immunoprecipitation assays. Tumor xenografts were constructed to confirm the function and mechanism of FOXD2-AS1 in chemosensitivity of DDP-resistant NSCLC.
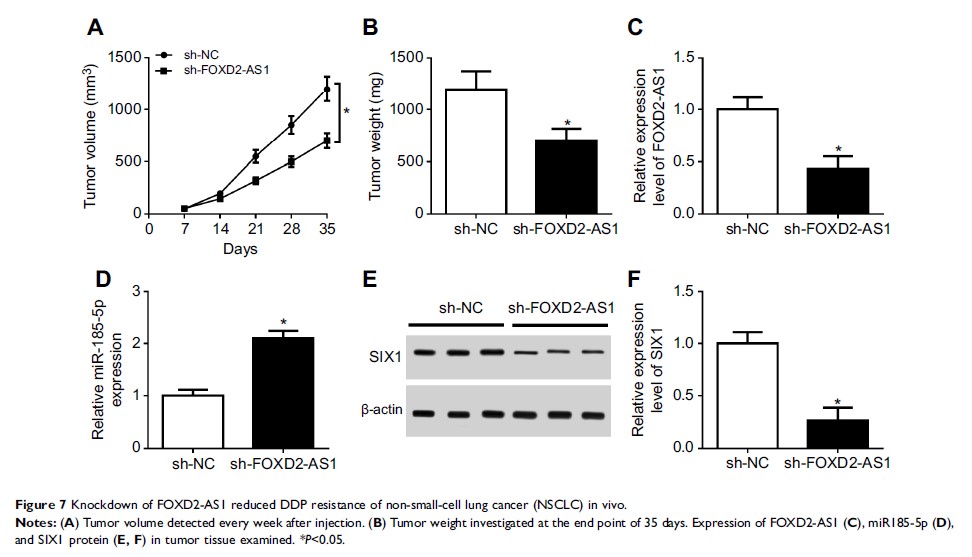
Results: FOXD2-AS1 and SIX1 were upregulated and miR185-5p downregulated in DDP-resistant NSCLC. Absence of FOXD2-AS1 enhanced drug sensitivity of A549/DDP and H1299/DDP cells, reflected by the reduced colony formation, cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and drug resistance–associated protein expression. FOXD2-AS1 acted as a molecular sponge for miR185-5p and relieved the binding of miR185-5p and its target gene SIX1 , leading to the derepression of SIX1 in A549/DDP and H1299/DDP cells. Rescue experiments validated the functional interaction among FOXD2-AS1, miR185-5p, and SIX1 . Moreover, FOXD2-AS1 interference receded the growth of DDP-resistant NSCLC tumors in vivo.
Conclusion: FOXD2-AS1/miR185-5p/SIX1 regulates the progression and chemosensitivity of DDP-resistant NSCLC, suggesting a potential therapeutic target for cisplatin-resistant NSCLC patients.
Keywords: FOXD2-AS1 , miR185-5p–SIX1, DDP resistance, NSCLC