108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

I-II 期鼻型自然杀伤 T 细胞淋巴瘤患者放疗方式的估计
Authors Liu X, Wu F, Guo Q, Wang Y, He Y, Luo H, Li Q, Zhong M, Li C, Yang H, Zhou J, Jin F
Received 14 January 2019
Accepted for publication 29 June 2019
Published 30 July 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 7219—7229
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S201514
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Nakshatri
Purpose: The objective of this study is to estimate radiotherapy (RT) modalities for patients with stage I-II nasal natural killer T-Cell lymphoma (NNKTCL), including plan quality, radiation delivery efficiency, cost of RT and excess absolute risk (EAR).
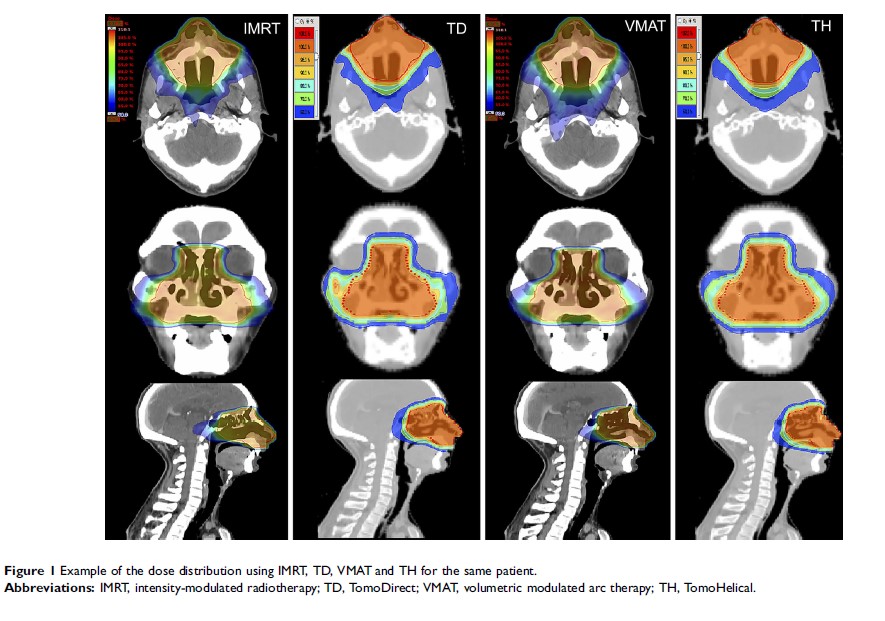
Materials and methods: Twenty-four representative patients with stage I-II NNKTCL treated with fix-field intensity-modulated radiotherapy (FF-IMRT) were re-planned for volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT), TomoDirect (TD) and TomoHelical (TH) on the TomoHDA system, respectively. Plan characteristics, cost of RT and EAR were compared.
Results: Compared with IMRT, TD and TH showed significant improvement in terms of D98%, D2%, cold spot volume and homogeneity index (HI) of planning target volume (PTV), while achieving worse Dmean and conformity index (CI). The mean dose of oropharynx, thyroid and left salivary, and the maximum dose of right salivary by TD (249.20%, p =0.000; 52.94%, p =0.000; 160.23%, p =0.022; 122.67%, p =0.027), VMAT (15.76%, p =0.000; 23.53%, p =0.000; 34.09%, p =0.000; 31.33%, p =0.000) and TH (250.32%, p =0.000; 58.82%, p =0.000; 120.45%, p =0.020; 117.33%, p =0.032) increased significantly compared to IMRT. VMAT reduced treatment time (p =0.000; 0.000; 0.000) and monitor units (MUs) (p =0.000; 0.000; 0.000) obviously compared with IMRT, TD and TH. The cost of RT for TD and TH increased 150% compared with IMRT and VMAT. IMRT obtained the lowest EAR to oropharynx, thyroid, left and right salivary gland in the four treatment modalities.
Conclusion: The results show that both TD and TH can achieve higher conformal target quality while getting worse organs at risk (OARs) sparing and EAR to some organs than IMRT for patients with stage I-II NNKTCL. IMRT delivers the lowest dose to most OARs, VMAT requires the lower cost of RT and shortest delivery time, and TH obtained the optimal target coverage. The results could provide direction for selecting proper RT modalities for different cases.
Keywords: nasal natural killer T-Cell lymphoma, excess absolute risk, IMRT, VMAT, TomoHelical