108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Nudol,一种来自金钗石斛的菲衍生物,诱导细胞周期停滞和细胞凋亡,并抑制骨肉瘤细胞的迁移
Authors Zhang Y, Zhang Q, Xin W, Liu N, Zhang H
Received 13 November 2018
Accepted for publication 10 June 2019
Published 29 July 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 2591—2601
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S180610
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Jianbo Sun
Purpose: Osteosarcoma is the most common malignancy of the bone in children and adolescents. There is an urgent need for the development of novel drugs to treat it. Nudol(1), a phenanthrene compound from the traditional Chinese medicine, Dendrobium nobile , exhibited antiproliferative activity against osteosarcoma cells. Therefore, the aim of the present study was to investigate the role and underlying mechanism of nudol(1) as potential chemotherapy for osteosarcoma.
Methods: Cell viability was determined by MTT assay. Cell-cycle phase distribution was analyzed by flow cytometry and Western blot. DAPI staining was used for morphology observation. Apoptosis was analysis via flow cytometry. The expression levels of mRNA and protein related to capase-mediated apoptotic pathway were detected by real-time PCR and western blotting. Migration was determined by wound healing assays.
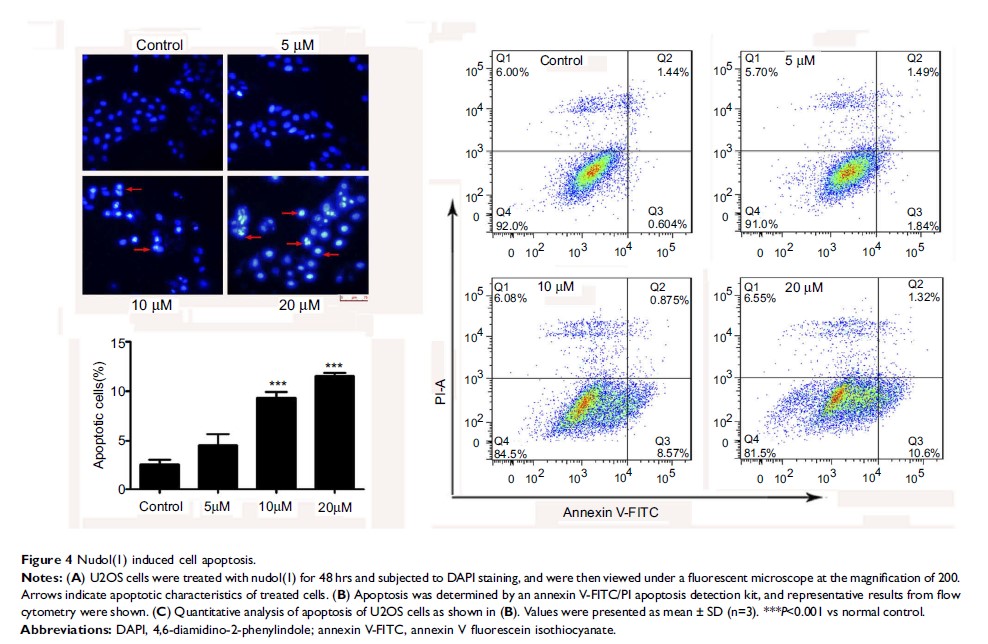
Results: Nudol(1) significantly decreased cell viability in several cancer cell lines. Moreover, nudol(1) caused cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase in U2OS cells, and it also induced cell apoptosis through the caspase-dependent pathway. In addition, treatment with nudol(1) suppressed the migration of U2OS cells.
Conclusion: The present study, for the first time, demonstrated effects of nudol(1) on OS in vitro and the potential molecular mechanisms. Accordingly, nudol(1) might have the potential for further development as a lead compound against bone tumor.
Keywords: nudol(1), phenanthrene, Dendrobium nobile , anti-proliferation, osteosarcoma