108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

黄芪甲苷 IV 通过 LOX-1/NLRP3 炎性体途径保护内皮祖细胞免受 ox-LDL 的损伤
Authors Qian W, Cai X, Qian Q, Zhuang Q, Yang W, Zhang X, Zhao L
Received 6 March 2019
Accepted for publication 29 May 2019
Published 29 July 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 2579—2589
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S207774
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Manfred Ogris
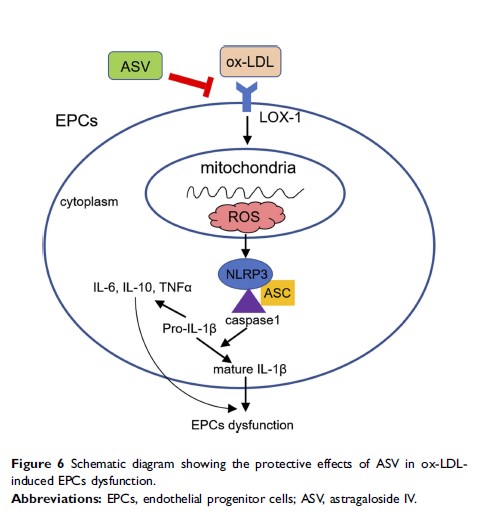
Purpose: Functional impairment of endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) is frequently observed in patients with diabetic vascular complications. Astragaloside IV (ASV) has a significant protective effect against vascular endothelial dysfunction. Thus, this study aimed to investigate the role of ASV on oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL)-induced EPCs dysfunction and its potential mechanisms.
Methods: EPCs were isolated from the peripheral blood of mice and treated with different concentration of ASV (10, 20, 40, 60, 80, 100 and 200 μM). ox-LDL was served as a stimulus for cell model. The proliferation and migration, and improved tube formation ability of EPCs were determined. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and the levels of inflammatory cytokines, including interleukin 1β (IL-1β), IL-6, IL-10 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) were measured. The expression oflectin-like oxidized LDL receptor (LOX-1) andNod-like receptor nucleotide-binding domain leucine rich repeat containing protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome were detected by Western blot analysis.
Results: We found ASV treatment alleviated ox-LDL-induced cellular dysfunction, as evidenced by promoted proliferation and migration, and improved tube formation ability. Besides, ASV treatment significantly suppressed ox-LDL-induced ROS production and the levels of inflammatory cytokines. ASV inhibited ox-LDL-induced expression of LOX-1 in a concentration-dependent manner. Overexpression of LOX-1 in EPCs triggered NLRP3inflammasome activation, while inhibition of LOX-1 or treatment with ASV suppressed ox-LDL-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Furthermore, overexpression of LOX-1 in ox-LDL-induced EPCs furtherly impaired cellular function, which could be ameliorated by ASV treatment.
Conclusion: Our study showed that ASV may protect EPCs against ox-LDL-induced dysfunction via LOX-1/NLRP3 pathway.
Keywords: endothelial progenitor cells, astragaloside IV, lectin-like oxidized LDL receptor, NLRP3 inflammasome