108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

血管生成素样蛋白 2 对 CHB 相关性肝细胞癌的诊断价值
Authors Zhou J, Yang W, Zhang S, He X, Lin J, Zhou T, Li Y, Wang G, Chen J
Received 27 May 2019
Accepted for publication 15 July 2019
Published 29 July 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 7159—7169
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S217170
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Eileen O'Reilly
Purpose: Angiopoietin-like protein 2 (ANGPTL2) is a secretory glycoprotein with various functions in vascular biology, inflammation and tumor development. As shown in our previous studies, ANGPTL2 expression positively correlates with liver fibrosis stages in chronic hepatitis B (CHB) patients. The aim of this study was further to assess whether ANGPTL2 represents a potential biomarker for detecting hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
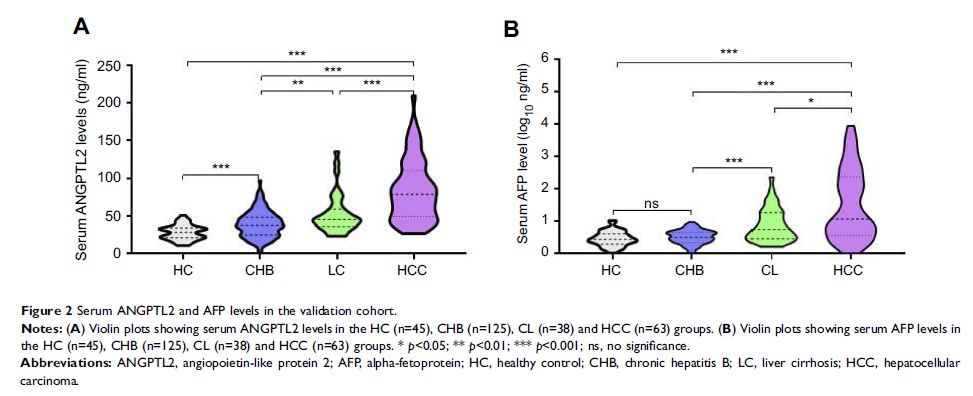
Patients and methods: This study enrolled 361 participants including healthy controls (HCs) and patients with CHB, liver cirrhosis (LC) and HCC. A discovery cohort consisted of 35 HCs and 55 patients with HCC. A total of 271 participants, including 45 HCs, 125 patients with CHB, 38 patients with LC, and 63 patients with HCC were enrolled in a validation cohort. Serum ANGPTL2 levels were detected using a human ANGPTL2 assay kit, and hepatic expression of ANGPTL2 was analyzed using immunohistochemistry.
Results: In the discovery cohort, a significantly higher serum ANGPTL2 level was detected in HCC than in HCs (73.49±33.87 vs 30.54±9.86; p <0.001). The results of the receiver operating characteristic curve indicated a significantly higher area under the curve for the ability of the ANGPTL2 to predict HCC than alpha fetoprotein (AFP). In the validation cohort, serum ANGPTL2 level gradually increased with the progression of chronic hepatitis B virus infection and reached the highest level in HCC. Immunohistochemical staining also confirmed these findings. The serum ANGPTL2 displayed better diagnostic efficiency not only for differentiating HCC from HC but also for differentiating HCC from high-risk controls (CHB+LC). Furthermore, the combination of ANGPTL2 and AFP may increase the diagnostic accuracy for HCC compared to ANGPTL2 or AFP alone. Importantly, ANGPTL2 levels also correlated with the detection of AFP-negative HCC.
Conclusions: ANGPTL2 may be used as a promising biomarker for the diagnosis of CHB-related HCC.
Keywords: ANGPTL2, CHB, HCC, diagnosis