108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

促红细胞生成素通过 Wnt/β-catenin 信号通路增强人牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化
Authors Zheng DH, Wang XX, Ma D, Zhang LN, Qiao QF, Zhang J
Received 1 May 2019
Accepted for publication 1 July 2019
Published 26 July 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 2543—2552
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S214116
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Melinda Thomas
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Qiongyu Guo
Objectives: The aim of this study is to examine the roles of erythropoietin (EPO) in regulating proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells (PDLSCs) and analyze the underlying signaling of these processes.
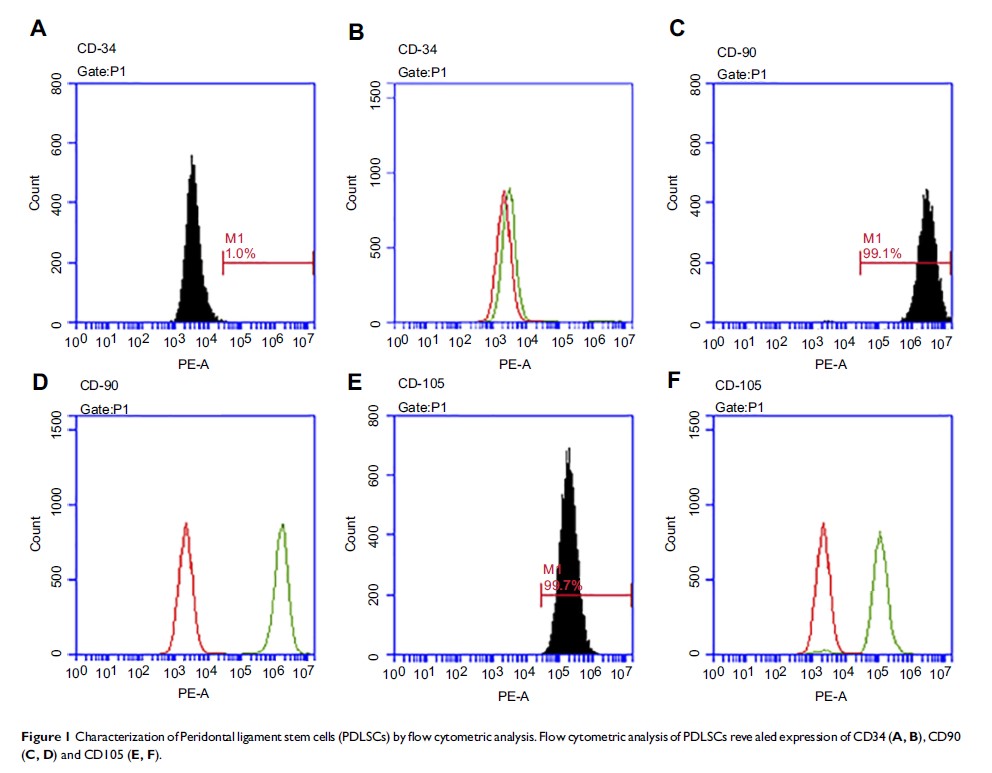
Materials and methods: PDLSCs were isolated and characterized. The PDLSCs were transfected with β-catenin shRNA. qRT-PCR and Western blot analysis were used to examine the osteogenic effects of EPO on the expression of osteogenic-related genes and protein (Runx2, OCN and Osterix) in PDLSCs. Alizarin Red-S staining was used to detect mineralized nodule formation. In addition, the relationship between the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and the effect of EPO on the osteogenesis of PDLSCs was investigated.
Results: The results suggested that EPO exerts positive osteogenic effects on PDLSCs. The results showed that EPO decreased the growth of PDLSCs slightly and increased alkaline phosphatase activity and calcium deposition in a dose-dependent manner. The expression of Runx2, Osterix and OCN was increased after EPO administration. EPO increases β-catenin and Cyclin D1 in PDLSCs. After transfected with β-catenin shRNA, the osteogenic effect of EPO on PDLSCs was attenuated.
Conclusion: EPO promotes osteogenic differentiation of PDLSCs. The underlying mechanism may be activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
Keywords: erythropoietin, periodontal ligament stem cell, osteogenesis, Wnt/β-catenin