108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

儿童 B 细胞和 T 细胞急性淋巴细胞白血病生物标志物的 iTRAQ 定量蛋白质表达谱分析
Authors Yu R, Zhang J, Zang Y, Zeng L, Zuo W, Bai Y, Liu Y, Sun K, Liu Y
Received 26 March 2019
Accepted for publication 18 June 2019
Published 25 July 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 7047—7063
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S210093
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Teng
Purpose: This study screened serum proteins to identify potential biomarkers for childhood B-cell and T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
Patients and methods: Serum collected from 20 newly diagnosed B-cell ALL, 20 T-cell ALL and 20 healthy children. The peptides from these samples were subjected to iTRAQ. Differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) were further validated by ELISA in 24 B-ALL, 24 T-ALL, and 24 healthy children.
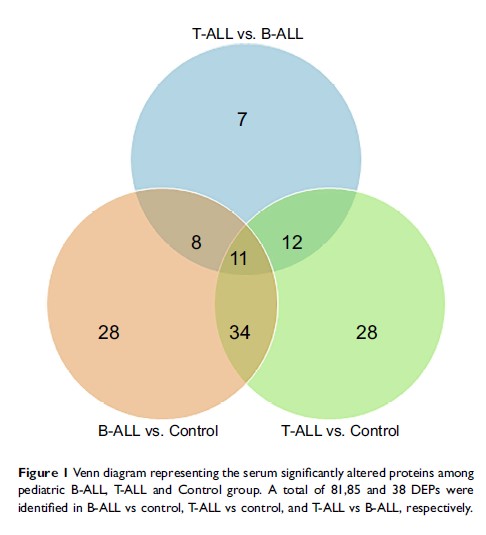
Results: Bioinformatics analysis revealed several pathways, including atherosclerosis signaling, interleukin signaling and production in macrophages and clathrin-mediated endocytosis signaling, that were closely related to childhood T-cell ALL. Furthermore, four selected proteins, namely LRG1, S100A8, SPARC and sL-selectin, were verified by ELISA. These results were consistent with the results of the proteomics analysis.
Conclusion: Serum S100A8 may serve as new diagnostic biomarkers in childhood B-cell ALL and T-cell ALL.
Keywords: B-cell ALL, T-cell ALL, proteomics, acute lymphoblastic leukemia, children, serum, isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation, ingenuity pathways analysis