108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

PEG 涂层和 Gd 负载荧光二氧化硅纳米粒子用于靶向前列腺癌的磁共振成像和荧光成像
Authors Jiang W, Fang H, Liu F, Zhou X, Zhao H, He X, Guo D
Received 28 February 2019
Accepted for publication 17 June 2019
Published 23 July 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 5611—5622
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S207098
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
Background: Multimodal imaging probes have become a powerful tool for improving detection sensitivity and accuracy, which are important in disease diagnosis and treatment.
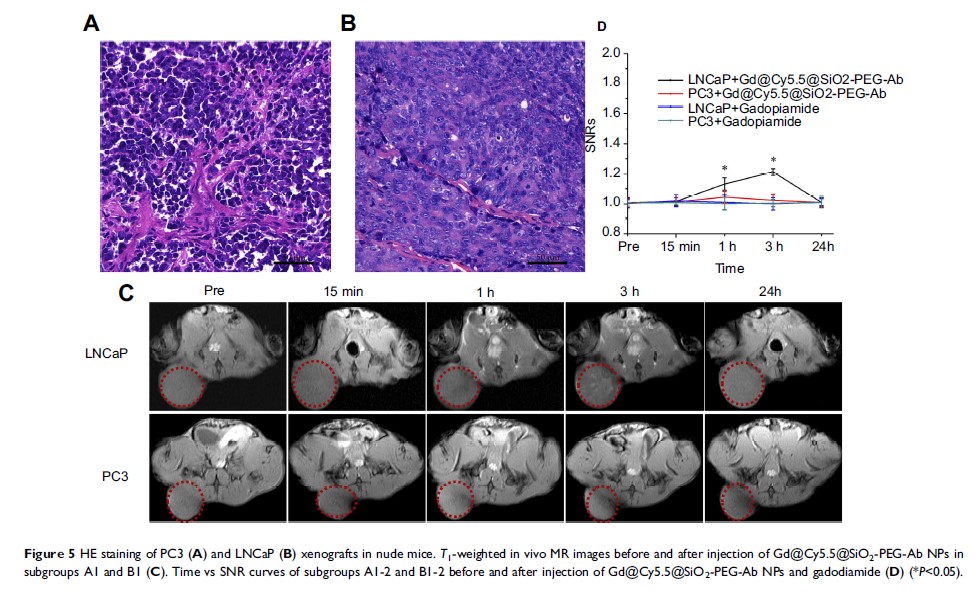
Methods: In this study, novel bifunctional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)/fluorescence probes were prepared by loading gadodiamide into fluorescent silica nanoparticles (NPs) (Gd@Cy5.5@SiO2-PEG-Ab NPs) for targeting of prostate cancer (PCa). The physicochemical characteristics, biosafety and PCa cell targeting ability of the Gd@Cy5.5@SiO2-PEG-Ab NPs were studied in vitro and in vivo.
Results: The Gd@Cy5.5@SiO2-PEG-Ab NPs had a spherical morphology with a relatively uniform size distribution and demonstrated high efficiency for Gd loading. In vitro and in vivo cell-targeting experiments demonstrated a high potential for the synthesized NPs to target prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) receptor-positive PCa cells, enabling MRI and fluorescence imaging. In vitro cytotoxicity assays and in vivo hematological and pathological assays showed that the prepared NPs exhibited good biological safety.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrates that the synthesized Gd@Cy5.5@SiO2-PEG-Ab NPs have great potential as MRI/fluorescence contrast agents for specific identification of PSMA receptor-positive PCa cells.
Keywords: silica nanoparticles, prostate cancer, magnetic resonance imaging, fluorescence imaging, targeting