108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

DNA 结合抑制剂 1(Id1)经由 Wnt/β-连环蛋白和 Shh 信号通路通过 Id1-c-Myc-PLAC8 轴介导结肠直肠癌细胞的干性
Authors Sun Y, Lai X, Yu Y, Li J, Cao L, Lin W, Huang C, Liao J, Chen W, Li C, Yang C, Ying M, Chen Q, Ye Y
Received 28 February 2019
Accepted for publication 15 June 2019
Published 23 July 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 6855—6869
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S207167
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ahmet Emre Eskazan
Background: Inhibitor of DNA binding 1 (Id1) is upregulated in multiple cancers, and Id1overexpression correlates with cancer aggressiveness and poor clinical outcomes in cancer patients. However, its roles in cancer stem-like cells (CSCs) and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) are still elusive.
Purpose: This study aimed to examine the role of Id1 on the mediation of CRC stemness and explore the underlying mechanisms.
Methods: Id1 and CD133 expression was detected by qPCR assay and immunohistochemistry (IHC) in normal mucosal and primary colorectal cancer (CRC) specimens. Id1 was stably knocked down (KD) in human CRC cell lines. Spheres forming assay and tumorigenic assay were performed to evaluate self-renewal capacity and tumor initiation. Expression of CSC- and EMT-related markers and TCF/LEF activity were assessed in HCT116 cells after Id1 KD.
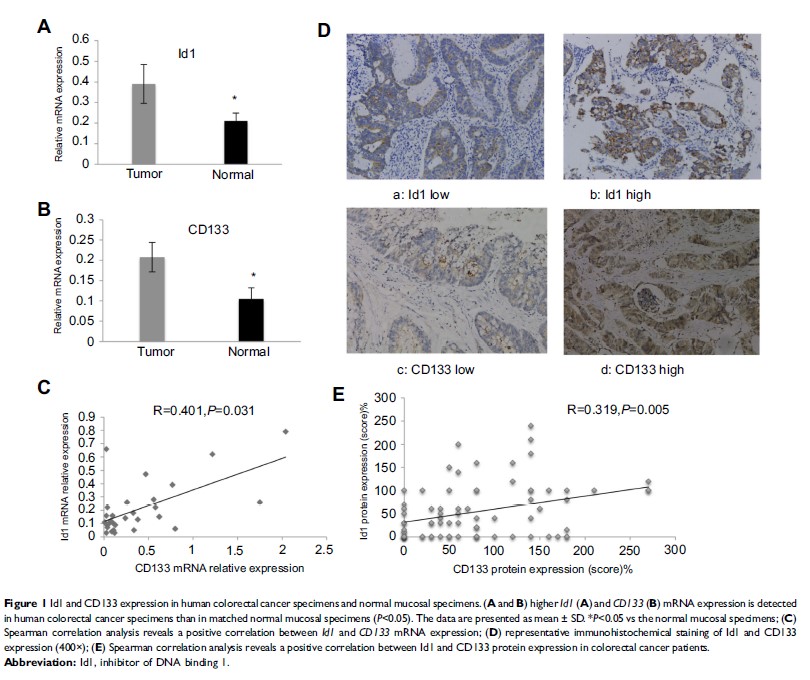
Results: qPCR assay showed higher Id1 and CD133 expression in CRC specimens than in normal mucosal specimens (P <0.05). IHC detected high cytoplasmic Id1 expression in 35 CRC specimens (46.7%), and high CD133 expression in 22 CRC specimens (29.3%) and negative expression in 18 normal mucosal specimens. High Id1 expression positively correlated with poor differentiation (P =0.034), and CD133 expression correlated with T category in CRC patients (P =0.002). Spearman correlation analysis revealed a positive correlation between Id1 and CD133 expression in CRC patients (P <0.05). Id1 KD resulted in suppression of proliferation, cell-colony formation, self-renewal capability and CSC-like features in HCT116 cells, and impaired the tumor-initiating capability in CRC cells. In addition, Id1 maintained the stemness of CRC cells via the Id1-c-Myc-PLAC8 axis through activating the Wnt/β-catenin and Shh signaling pathways.
Conclusions: Id1 expression significantly correlates with CD133 expression in CRC patients, and Id1 KD impairs CSC-like capacity and reverses EMT traits, partially via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Id1 may be a promising therapeutic target against colon CSCs.
Keywords: inhibitor of DNA binding 1, Id1, self-renewal, stemness, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, colon cancer, Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway