109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

使用表达图谱对与多发性骨髓瘤的浆细胞相关的关键基因进行鉴定
Published Date July 2015 Volume 2015:8 Pages 1795—1803
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S80075
Received 30 December 2014, Accepted 6 March 2015, Published 20 July 2015
Objective: To uncover
the potential regulatory mechanisms of the relevant genes that contribute to
the prognosis and prevention of multiple myeloma (MM).
Methods: Microarray data
(GSE13591) were downloaded, including five plasma cell samples from normal
donors and 133 plasma cell samples from MM patients. Differentially expressed
genes (DEGs) were identified by Student’s t -test.
Functional enrichment analysis was performed for DEGs using the Gene Ontology
(GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) databases.
Transcription factors and tumor-associated genes were also explored by mapping
genes in the TRANSFAC, the tumor suppressor gene (TSGene), and tumor-associated
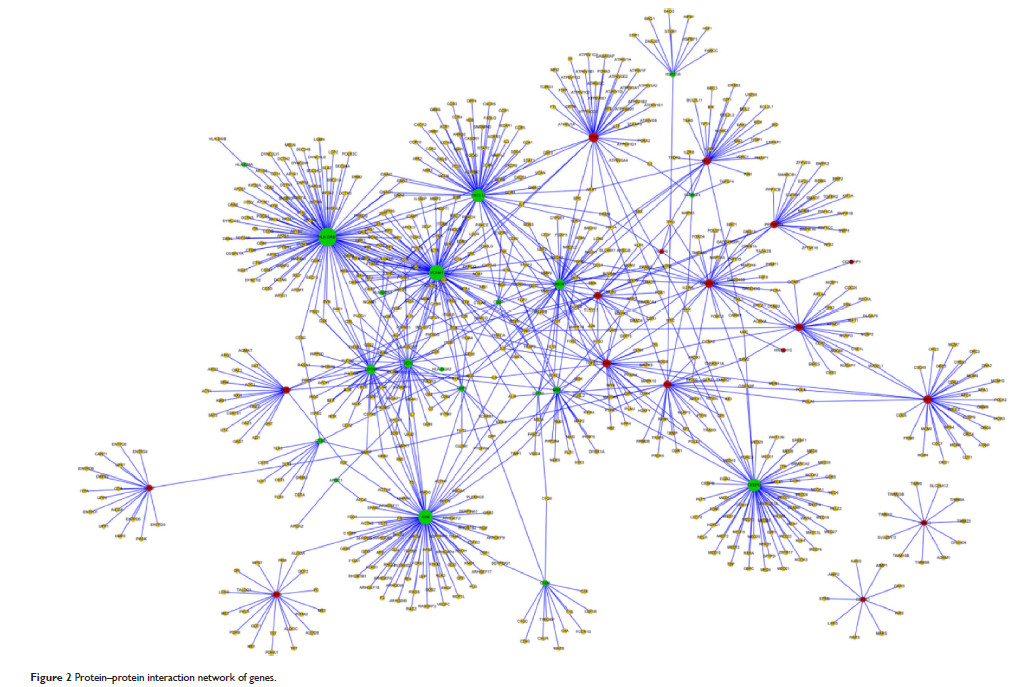
gene (TAG) databases. A protein–protein interaction (PPI) network and PPI
subnetworks were constructed by Cytoscape software using the Search Tool for
the Retrieval of Interacting Genes (STRING) database.
Results: A total of 63 DEGs (42
downregulated, 21 upregulated) were identified. Functional enrichment analysis
showed that HLA-DRB1 and VCAM1 might be involved in the
positive regulation of immune system processes, and HLA-DRB1 might be related to the intestinal immune network for IgA production pathway.
The genes CEBPD , JUND ,
and ATF3 were identified as
transcription factors. The top ten nodal genes in the PPI network were revealed
including HLA-DRB1 , VCAM1 , and TFRC . In addition, genes in the PPI
subnetwork, such as HLA-DRB1 and VCAM1 , were enriched in the cell
adhesion molecules pathway, whereas CD4 and TFRC were both enriched in the
hematopoietic cell pathway.
Conclusion: Several crucial
genes correlated to MM were identified, including CD4 , HLA-DRB1 , TFRC , and VCAM1 , which might exert their
roles in MM progression via immune-mediated pathways. There might be certain
regulatory correlations between HLA-DRB1 , CD4 , and TFRC .
Keywords: multiple myeloma,
functional enrichment, transcription factor analysis, PPI network, pathway
enrichment