109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
MMP7 蛋白表达对食管癌的临床病理学意义: 一项综合分析
Authors Miao S, Zhou SY, Han CS, Zhang LN, Sun HB, Yang B
Published Date July 2015 Volume 2015:9 Pages 3729—3740
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S85987
Received 2 April 2015, Accepted 14 May 2015, Published 20 July 2015
Background: The MMP-7 basement membrane and extracellular matrix may be essential
for tumor invasion and metastasis, and the results presented herein showed a
relationship between MMP-7 expression and esophageal cancer (EC). However, its
clinicopathological value for EC patients remains inconsistent. To clarify
their associations, a meta-analysis of the relevant published literature was
conducted.
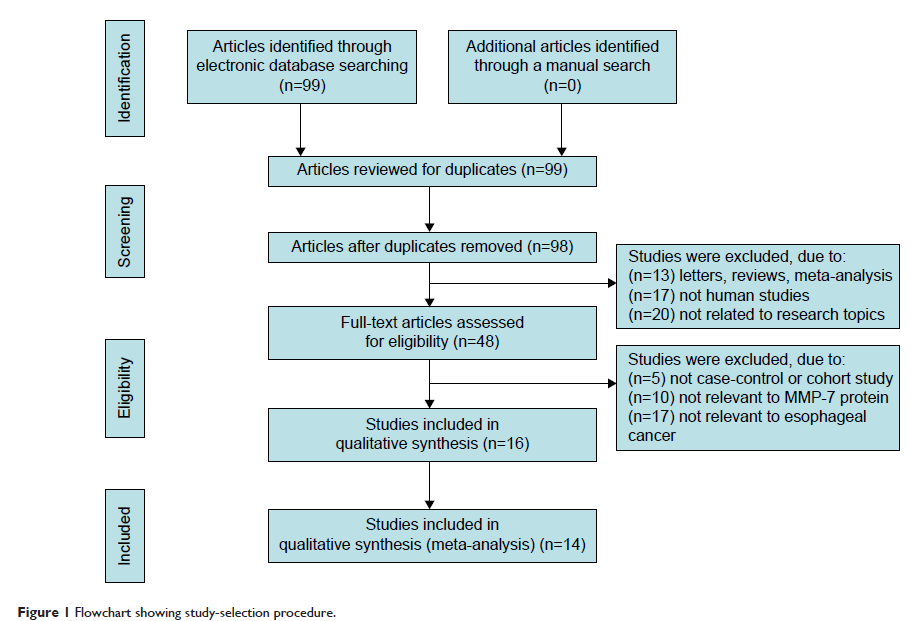
Materials and methods: Databases including PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, CISCOM, CINAHL, and Google Scholar were electronically searched. Only those studies analyzing MMP-7 expression in EC patients with regard to series of different demographic variables and clinicopathological stages (TNM stage, differentiation and invasion grade, and lymph-node [LN] metastasis) were eligible for inclusion. Summary odds ratios (ORs) were pooled in accordance with the random-effect model.
Results: Fourteen clinical cohort studies (tumor samples =935) were incorporated into the current meta-analysis. Results revealed that increased MMP-7 expression in EC patients was positively correlated to TNM stage III–IV (OR 3.04, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.43–6.46; P =0.004). Similar connections were also detected in the differentiation grade, invasion grade, and LN metastasis (all P <0.05). Country-stratified analysis yielded significant association of elevated MMP-7 expression with EC in the People’s Republic of China (PRC) under both TNM III–IV versus I–II and differentiation low versus high comparisons (TNM stage, OR 2.01, 95% CI 1.55–2.59, P <0.001; differentiation grade, OR 1.32, 95% CI 1.11–1.57, P =0.002). With regard to invasion grade and LN metastasis, significant association was observed in all the experimental subgroups (all P -values [PRC and Japan] were lower than 0.05).
Conclusion: These data showed an obvious connection between MMP-7 and TNM stages, differentiation grade, invasive grade, and LN metastasis of EC, indicating that overexpression of MMP-7 may be a suitable diagnostic biomarker for variation in EC clinicopathological features.
Keywords: MMP-7, esophagus carcinoma, statistical analysis
Materials and methods: Databases including PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, CISCOM, CINAHL, and Google Scholar were electronically searched. Only those studies analyzing MMP-7 expression in EC patients with regard to series of different demographic variables and clinicopathological stages (TNM stage, differentiation and invasion grade, and lymph-node [LN] metastasis) were eligible for inclusion. Summary odds ratios (ORs) were pooled in accordance with the random-effect model.
Results: Fourteen clinical cohort studies (tumor samples =935) were incorporated into the current meta-analysis. Results revealed that increased MMP-7 expression in EC patients was positively correlated to TNM stage III–IV (OR 3.04, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.43–6.46; P =0.004). Similar connections were also detected in the differentiation grade, invasion grade, and LN metastasis (all P <0.05). Country-stratified analysis yielded significant association of elevated MMP-7 expression with EC in the People’s Republic of China (PRC) under both TNM III–IV versus I–II and differentiation low versus high comparisons (TNM stage, OR 2.01, 95% CI 1.55–2.59, P <0.001; differentiation grade, OR 1.32, 95% CI 1.11–1.57, P =0.002). With regard to invasion grade and LN metastasis, significant association was observed in all the experimental subgroups (all P -values [PRC and Japan] were lower than 0.05).
Conclusion: These data showed an obvious connection between MMP-7 and TNM stages, differentiation grade, invasive grade, and LN metastasis of EC, indicating that overexpression of MMP-7 may be a suitable diagnostic biomarker for variation in EC clinicopathological features.
Keywords: MMP-7, esophagus carcinoma, statistical analysis