109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
带有黑腹果蝇 (Drosophila melanogaster ) 脱氧核苷激酶和核苷类似物的腺病毒在体内和体外对人乳腺癌的协同抗癌效应
Authors Tang M, Zu C, He AN, Wang WQ, Chen B, Zheng XY
Published Date July 2015 Volume 2015:9 Pages 3301—3312
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S81717
Received 28 January 2015, Accepted 27 February 2015, Published 14 July 2015
Background: Suicide gene therapy in cancer can selectively kill tumors without
damaging normal tissues. Drosophila melanogaster multisubstrate deoxyribonucleoside kinase (Dm -dNK), an
original suicide kinase, makes use of the carcinomatous suicide gene therapy
for broader substrate specificity and a higher catalytic rate.
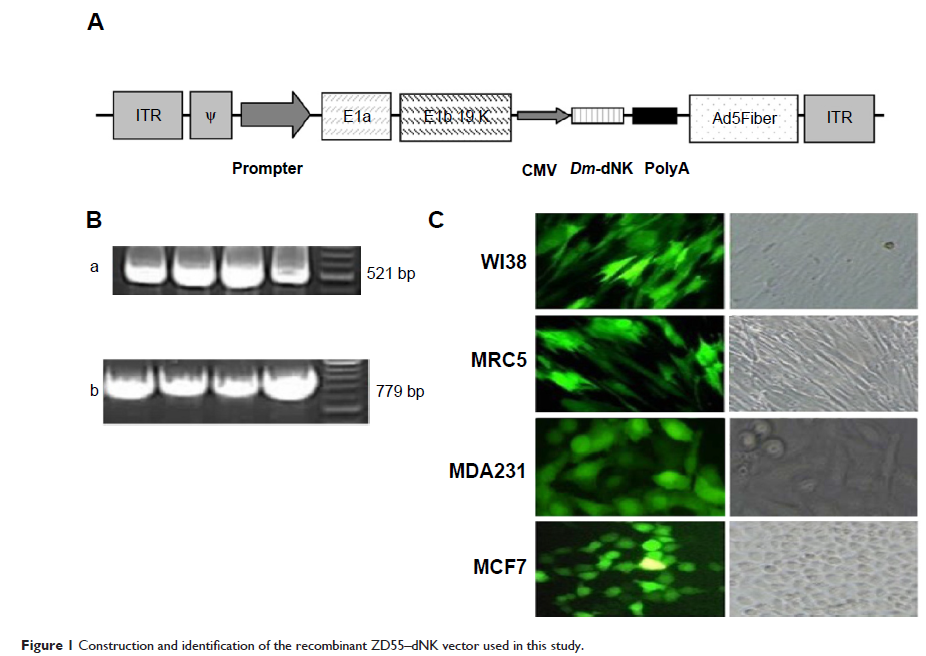
Methods: To enhance the anti-tumor efficacy of Dm -dNK and maintain its substrate specificity and safety control in the meantime, the conditionally replicative gene–viral system, ZD55–dNK (which contains the selective replication adenovirus, ZD55, encoded with Dm -dNK), was investigated in pushing a deeper development of this strategy. Selective replication, cell killing efficacy, and cytotoxicity, in combination with chemotherapy, were applied to two breast cell lines (MDA231 and MCF7 cells), two normal cell lines (WI38 and MRC5 cells), and the MCF7 xenograft model in vivo.
Results: The preclinical study showed that ZD55–dNK, combined with 2',2'-difluorodeoxycytidine (DFDC), synergistically inhibited adenovirus replication in vitro but maintained specifically cancer cell killing efficacy. ZD55–dNK also greatly improved the antineoplastic effect in vitro and in breast cancer xenograft in vivo.
Conclusion: The concomitant use of ZD55–dNK and DFDC is possibly a novel and promising approach to breast cancer treatment, and further investigation on the safe control of excessive virus replication and the efficacy of this approach in humans is warranted.
Keywords: Dm -dNK, oncolytic adenovirus, cancer suicide gene therapy, nucleoside analogs, safety control
Methods: To enhance the anti-tumor efficacy of Dm -dNK and maintain its substrate specificity and safety control in the meantime, the conditionally replicative gene–viral system, ZD55–dNK (which contains the selective replication adenovirus, ZD55, encoded with Dm -dNK), was investigated in pushing a deeper development of this strategy. Selective replication, cell killing efficacy, and cytotoxicity, in combination with chemotherapy, were applied to two breast cell lines (MDA231 and MCF7 cells), two normal cell lines (WI38 and MRC5 cells), and the MCF7 xenograft model in vivo.
Results: The preclinical study showed that ZD55–dNK, combined with 2',2'-difluorodeoxycytidine (DFDC), synergistically inhibited adenovirus replication in vitro but maintained specifically cancer cell killing efficacy. ZD55–dNK also greatly improved the antineoplastic effect in vitro and in breast cancer xenograft in vivo.
Conclusion: The concomitant use of ZD55–dNK and DFDC is possibly a novel and promising approach to breast cancer treatment, and further investigation on the safe control of excessive virus replication and the efficacy of this approach in humans is warranted.
Keywords: Dm -dNK, oncolytic adenovirus, cancer suicide gene therapy, nucleoside analogs, safety control