109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
将肽 T7 及其衍生物作为整合素 αvβ3 靶向显像剂的探索
Authors He X, Hao Y, Long W, Song N, Fan S, Meng A
Published Date June 2015 Volume 2015:8 Pages 1483—1491
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S82095
Received 2 February 2015, Accepted 29 April 2015, Published 15 June 2015
Approved for publication by Professor Jianmin Xu
Objective: The aim of the present study was to develop potential candidates of integrin αvβ3-targeted imaging agent, which can facilitate the diagnosis and treatment of malignant solid tumors.
Methods: Peptides derived from tumstatin, named T7 and T7-6H, were derivatized to contain histidine in the C-terminus of their sequence and were labeled with 99mTc via nitrido and carbonyl precursors. The radiochemical purity and stability of 99mTc-labeled T7 and T7-6H were characterized by thin-layer chromatography. The whole body biodistribution was studied in NCI-H157-bearing BALB/c nude mice.
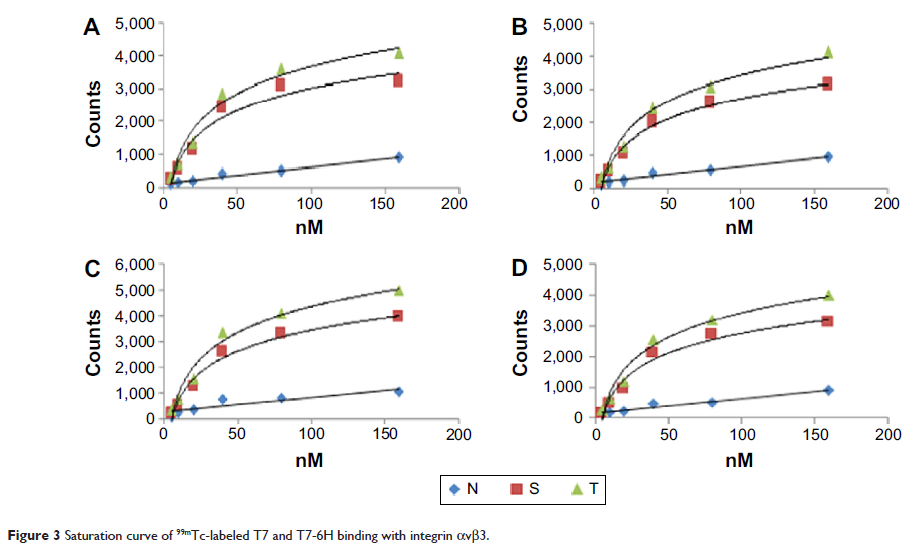
Results: The 99mTc-labeled T7 and T7-6H showed adequate in vitro stability, with a high radiochemical purity of over 90%. The dissociation constant (Kd) value of the 99mTc-labeled T7 and T7-6H ranged from 68.5 nM to 140.8 nM in U251 and NCI-H157 cell lines. 99mTc-labeled T7 and T7-6H showed no significant difference of biodistribution in mice. Furthermore, both T7 and T7-6H exhibited a poor blood–brain barrier penetration and a transient accumulation in lung; the uptake in tumor tissues was significantly higher than in muscle tissue, with a ratio of 5.8.
Conclusion: 99mTc-labeled T7 and T7-6H can be regarded as promising single-photon emission computed tomography probes for imaging integrin αvβ3, and need to be further studied for noninvasive detection of tumors.
Keywords: integrin, angiogenesis, ligands
Methods: Peptides derived from tumstatin, named T7 and T7-6H, were derivatized to contain histidine in the C-terminus of their sequence and were labeled with 99mTc via nitrido and carbonyl precursors. The radiochemical purity and stability of 99mTc-labeled T7 and T7-6H were characterized by thin-layer chromatography. The whole body biodistribution was studied in NCI-H157-bearing BALB/c nude mice.
Results: The 99mTc-labeled T7 and T7-6H showed adequate in vitro stability, with a high radiochemical purity of over 90%. The dissociation constant (Kd) value of the 99mTc-labeled T7 and T7-6H ranged from 68.5 nM to 140.8 nM in U251 and NCI-H157 cell lines. 99mTc-labeled T7 and T7-6H showed no significant difference of biodistribution in mice. Furthermore, both T7 and T7-6H exhibited a poor blood–brain barrier penetration and a transient accumulation in lung; the uptake in tumor tissues was significantly higher than in muscle tissue, with a ratio of 5.8.
Conclusion: 99mTc-labeled T7 and T7-6H can be regarded as promising single-photon emission computed tomography probes for imaging integrin αvβ3, and need to be further studied for noninvasive detection of tumors.
Keywords: integrin, angiogenesis, ligands