109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
使用芪参益气丸® (QiShenYiQi Pill®) 使多个线粒体功能障碍好转,从而保护心肌免受缺血/再灌注性损伤
Authors Chen JR, Wei J, Wang LY, Zhu Y, Li L, Olunga MA, Gao XM, Fan GW
Published Date June 2015 Volume 2015:9 Pages 3051—3066
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S82146
Received 3 February 2015, Accepted 25 March 2015, Published 15 June 2015
Approved for publication by Professor Shu-Feng Zhou
Aim: To investigate the potential cardioprotective effects of QiShenYiQi Pill® (QSYQ) on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury through antioxidative stress and mitochondrial protection.
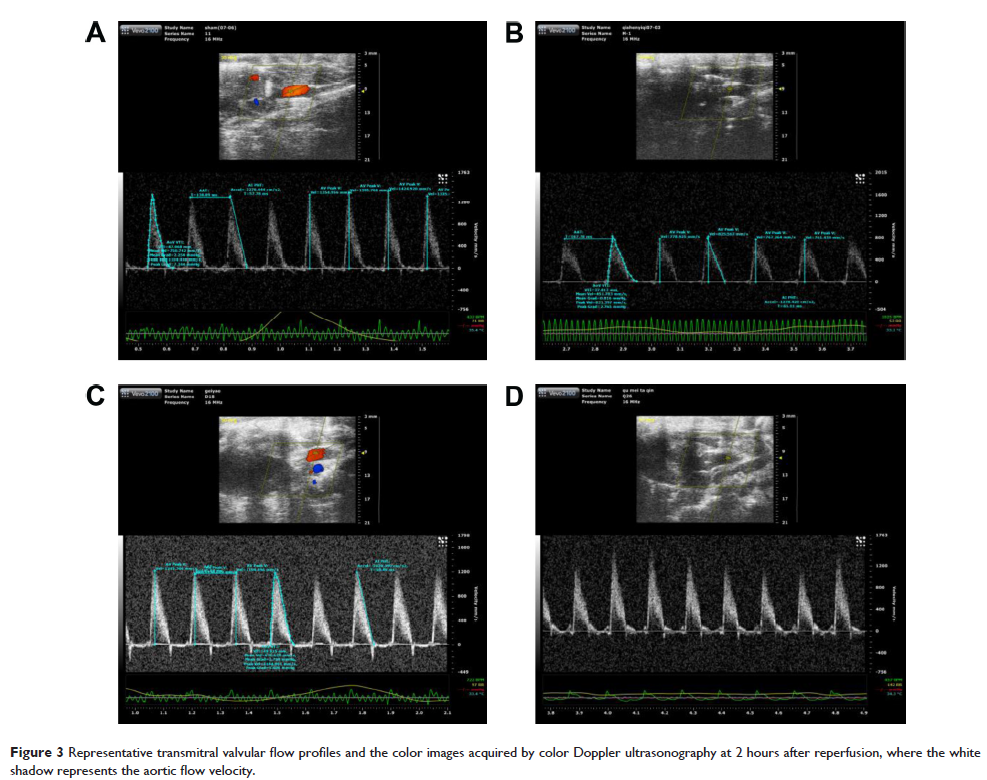
Methods and results: Sprague Dawley rats were pretreated with QSYQ or saline for 7 days and subjected to ischemia (30 minutes occlusion of the left anterior descending coronary artery) and reperfusion (120 minutes). Cardiac functions were evaluated by echocardiogram and hemodynamics. Myocardial mitochondria were obtained to evaluate changes in mitochondrial structure and function, immediately after 120 minutes reperfusion. Pretreatment with QSYQ protected against I/R-induced myocardial structural injury and improved cardiac hemodynamics, as demonstrated by normalized serum creatine kinase and suppressed oxidative stress. Moreover, the impaired myocardial mitochondrial structure and function decreased level of ATP (accompanied by reduction of ATP5D and increase in the expression of cytochrome C). Myocardial fiber rupture, interstitial edema, and infiltrated leukocytes were all significantly ameliorated by pretreatment with QSYQ.
Conclusion: Pretreatment of QSYQ in Sprague Dawley rats improves ventricular function and energy metabolism and reduces oxidative stress via ameliorating multiple mitochondrial dysfunctions during I/R injury.
Keywords: QSYQ, ischemia/reperfusion injury, energy metabolism, mitochondria
Methods and results: Sprague Dawley rats were pretreated with QSYQ or saline for 7 days and subjected to ischemia (30 minutes occlusion of the left anterior descending coronary artery) and reperfusion (120 minutes). Cardiac functions were evaluated by echocardiogram and hemodynamics. Myocardial mitochondria were obtained to evaluate changes in mitochondrial structure and function, immediately after 120 minutes reperfusion. Pretreatment with QSYQ protected against I/R-induced myocardial structural injury and improved cardiac hemodynamics, as demonstrated by normalized serum creatine kinase and suppressed oxidative stress. Moreover, the impaired myocardial mitochondrial structure and function decreased level of ATP (accompanied by reduction of ATP5D and increase in the expression of cytochrome C). Myocardial fiber rupture, interstitial edema, and infiltrated leukocytes were all significantly ameliorated by pretreatment with QSYQ.
Conclusion: Pretreatment of QSYQ in Sprague Dawley rats improves ventricular function and energy metabolism and reduces oxidative stress via ameliorating multiple mitochondrial dysfunctions during I/R injury.
Keywords: QSYQ, ischemia/reperfusion injury, energy metabolism, mitochondria