109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
肝移植后金黄色葡萄球菌 (Staphylococcus aureus ) 败血症: 对 20 个病例的临床分析
Authors Zhou JD, Huang H, Liu S, Yu P, Wan QQ
Published Date June 2015 Volume 2015:11 Pages 933—937
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S84579
Received 13 March 2015, Accepted 17 April 2015, Published 12 June 2015
Approved for publication by Professor Deyun Wang
Background: To describe the incidence, clinical characteristics, and outcomes of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia after liver transplantation and investigate the drug resistance of S. aureus to frequently used antibiotics to provide evidence for clinical prevention and therapy.
Materials and methods: In a double-center retrospective study, blood cultures positive for S. aureus were obtained from January 1, 2001 to December 31, 2014. The BACTEC 9120 blood culture system and the Vitek-2 system were used to process blood samples and identify species, respectively. We also collected these patients’ data to confirm clinical and laboratory characteristics.
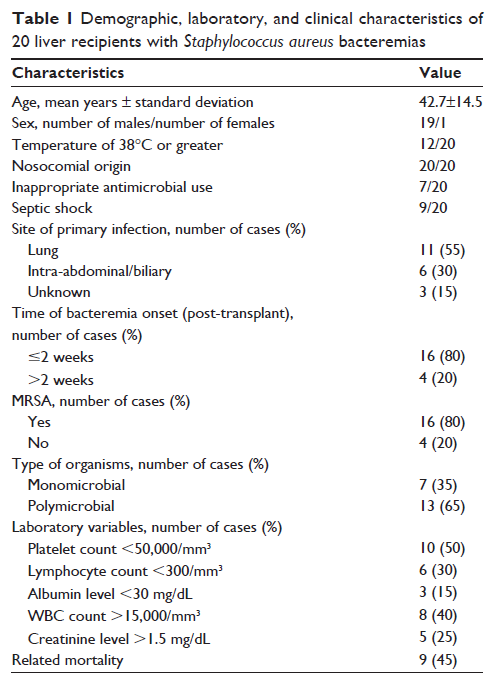
Results: Twenty of 275 (7.3%) liver recipients developed S. aureus bacteremia during the study period. The median time to the onset of S. aureus bacteremias was 6 days after liver transplantation and all episodes of bacteremias were early onset. The lung was the most common source of primary infection, followed by the intra-abdominal/biliary tract. A total of nine (45%) liver recipients died due to S. aureus bacteremias. Of these 20 S. aureus cases, 80% were methicillin-resistant. S. aureuswas highly resistant to erythromycin and penicillin (resistance rate >90%). No S. aureus resistant to glycopeptides and oxazolidone antibiotics was observed. There were seven (35%) liver recipients with an inappropriate antibiotic therapy. Between the periods of 2001–2007 and 2008–2014, the distribution of methicillin-resistant S. aureus was not significantly different (P =1.000). Pneumonia as a predominant primary source, a high body temperature, abnormal blood pressure, and decreased platelets, which occurred in the early period after liver transplantation, as well as high morbidity and mortality, were the main characteristics of S. aureus bacteremias.
Conclusion: S. aureus led to severe bacteremias in liver recipients, with high morbidity and mortality, and the majority of them comprised methicillin-resistant S. aureus .
Keywords: liver transplantation, Staphylococcus aureus , bacteremia, drug resistance
Materials and methods: In a double-center retrospective study, blood cultures positive for S. aureus were obtained from January 1, 2001 to December 31, 2014. The BACTEC 9120 blood culture system and the Vitek-2 system were used to process blood samples and identify species, respectively. We also collected these patients’ data to confirm clinical and laboratory characteristics.
Results: Twenty of 275 (7.3%) liver recipients developed S. aureus bacteremia during the study period. The median time to the onset of S. aureus bacteremias was 6 days after liver transplantation and all episodes of bacteremias were early onset. The lung was the most common source of primary infection, followed by the intra-abdominal/biliary tract. A total of nine (45%) liver recipients died due to S. aureus bacteremias. Of these 20 S. aureus cases, 80% were methicillin-resistant. S. aureuswas highly resistant to erythromycin and penicillin (resistance rate >90%). No S. aureus resistant to glycopeptides and oxazolidone antibiotics was observed. There were seven (35%) liver recipients with an inappropriate antibiotic therapy. Between the periods of 2001–2007 and 2008–2014, the distribution of methicillin-resistant S. aureus was not significantly different (P =1.000). Pneumonia as a predominant primary source, a high body temperature, abnormal blood pressure, and decreased platelets, which occurred in the early period after liver transplantation, as well as high morbidity and mortality, were the main characteristics of S. aureus bacteremias.
Conclusion: S. aureus led to severe bacteremias in liver recipients, with high morbidity and mortality, and the majority of them comprised methicillin-resistant S. aureus .
Keywords: liver transplantation, Staphylococcus aureus , bacteremia, drug resistance