109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
SORL1 基因多态性与中国汉族人群的散发性阿尔茨海默病 (Alzheimer's disease) 之间关联的探索性分析
Authors Zhang F, Liu X, Wang B, Cheng Z, Zhao X, Zhu J, Wang D, Wang Y, Dong A, Li P, Jin C
Published Date June 2015 Volume 2015:11 Pages 1443—1448
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S85370
Received 24 March 2015, Accepted 24 April 2015, Published 12 June 2015
Approved for publication by Professor Wai Kwong Tang
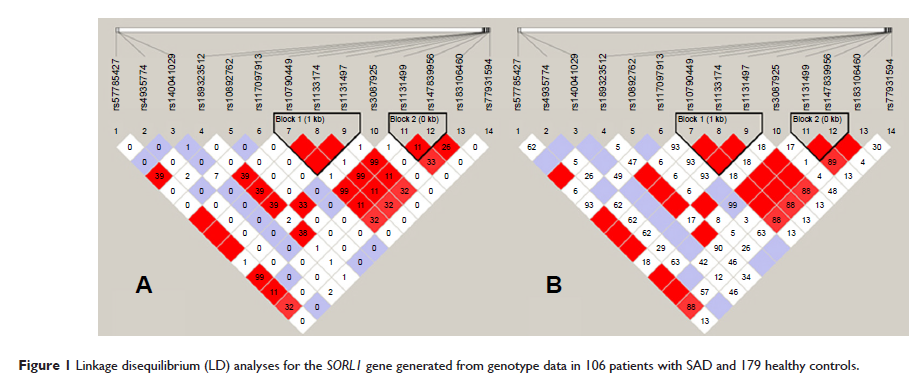
Abstract: In previous studies, we reported that the sortilin-related receptor, L (DLR class) A repeats containing (SORL1 ) gene single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are associated with the risk of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease (SAD) in the Han Chinese population. To further explore the relationships between SORL1 genetic variants and SAD, we conducted a two-step study. Sequencing analysis in 50 case samples identified 14 SNPs within the promoter and untranslated region of the SORL1 gene. Subsequent genotyping analysis in 106 patients with SAD and 179 healthy controls detected a significant association between the “G” allele of SNP rs1133174 in the 3' untranslated region of the SORL1 gene and SAD risk (odds ratio =1.92, 95% confidence interval [95% CI] =1.28–2.90, adjusted P =0.028). In addition, “G” allele carriers of rs1133174 (GA + GG) have a 2.15-fold increased risk of SAD compared to noncarriers (AA) (adjusted P =0.042). However, no significant positive associations were observed in the other 13 SNPs within the SORL1 gene. These preliminary findings suggest that the SORL1 SNP rs1133174 may be a potential risk locus for SAD in the Han Chinese population.
Keywords: SORL1 , Alzheimer’s disease, polymorphism, Han Chinese, association
Keywords: SORL1 , Alzheimer’s disease, polymorphism, Han Chinese, association