109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
结膜下注射 VEGF 抑制剂 (贝伐单抗 Bevacizumab) 在治疗干眼症的疗效和安全性
Authors Jiang X, Lv H, Qiu W, Liu Z, Li X, Wang W
Published Date June 2015 Volume 2015:9 Pages 3043—3050
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S85529
Received 26 March 2015, Accepted 22 April 2015, Published 12 June 2015
Approved for publication by Professor Shu-Feng Zhou
Purpose: Dry eye is a chronic inflammatory ocular surface disease with high prevalence. The current therapies for dry eye remain to be unspecific and notcomprehensive. This study aims to explore safety and efficacy of a novel treatment – subconjunctival injection of bevacizumab – in dry eye patients.
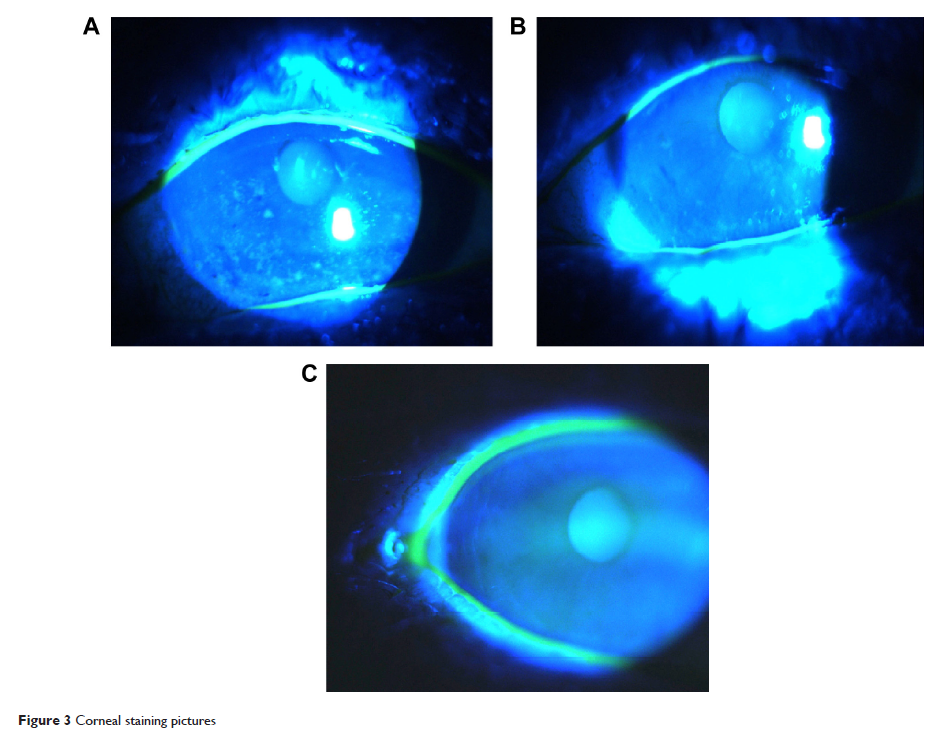
Methods: Sixty-four eyes of 32 dry eye patients received subconjunctival injection of 100 μL 25 mg/mL bevacizumab. Dry eye symptoms, signs (corrected visual acuity, intraocular pressure, conjunctival vascularity, corneal staining, tear break-up time, Marx line score, and blood pressure), and conjunctival impression cytology were evaluated 3 days before and 1 week, 1 month, and 3 months after injection.
Results: Significant improvements were observed in dry eye symptoms, tear break-up time, and conjunctival vascularization area at all the visits after injection compared to the baseline (P <0.05). The density of the goblet cell increased significantly at 1 month and 3 months after injection (P <0.05). There was no visual and systemic threat observed in any patient.
Conclusion: Subconjunctival injection of 100 µL 25 mg/mL bevacizumab is a safe and efficient treatment for ocular surface inflammation of dry eye disease.
Keywords: anti-VEGF, bevacizumab, dry eye, ocular surface inflammation, subconjunctival
Methods: Sixty-four eyes of 32 dry eye patients received subconjunctival injection of 100 μL 25 mg/mL bevacizumab. Dry eye symptoms, signs (corrected visual acuity, intraocular pressure, conjunctival vascularity, corneal staining, tear break-up time, Marx line score, and blood pressure), and conjunctival impression cytology were evaluated 3 days before and 1 week, 1 month, and 3 months after injection.
Results: Significant improvements were observed in dry eye symptoms, tear break-up time, and conjunctival vascularization area at all the visits after injection compared to the baseline (P <0.05). The density of the goblet cell increased significantly at 1 month and 3 months after injection (P <0.05). There was no visual and systemic threat observed in any patient.
Conclusion: Subconjunctival injection of 100 µL 25 mg/mL bevacizumab is a safe and efficient treatment for ocular surface inflammation of dry eye disease.
Keywords: anti-VEGF, bevacizumab, dry eye, ocular surface inflammation, subconjunctival