109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
对慢性阻塞性肺病 (COPD) 中基因表达模式的综合分析
Authors Wei L, Xu D, Qian YC, Huang GY, Ma W, Liu FY, Shen YH, Wang ZF, Li L, Zhang SF, Chen YF
Published Date June 2015 Volume 2015:10(1) Pages 1103—1109
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S68570
Received 29 May 2014, Accepted 31 July 2014, Published 10 June 2015
Approved for publication by Dr Richard Russell
Objective: To investigate the gene-expression profile of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients and explore the possible therapeutic targets.
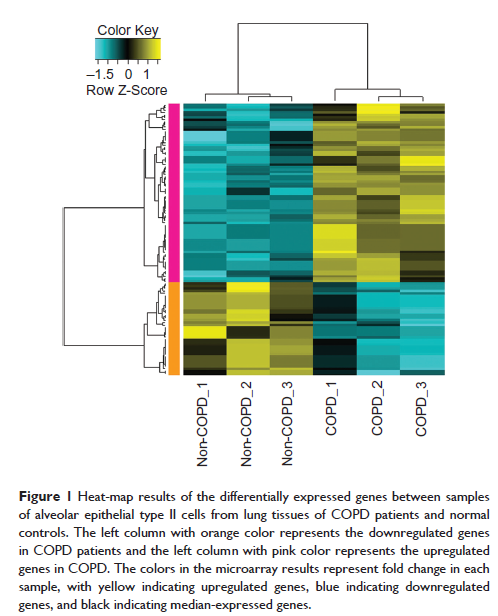
Methods: The microarray raw dataset GSE29133, including three COPD samples and three normal samples, was obtained from Gene Expression Omnibus. After data preprocessing with the Affy package, Student’s t -test was employed to identify the differentially expressed genes (DEGs). The up- and downregulated DEGs were then pooled for gene-ontology and pathway-enrichment analyses using the Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery (DAVID). The upstream regulatory elements of these DEGs were also explored by using Whole-Genome rVISTA. Furthermore, we constructed a protein–protein interaction (PPI) network for DEGs. The surfactant protein D (SP-D) serum level and HLA-A gene frequency in COPD patients and healthy controls were also measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and real-time polymerase chain reaction, respectively.
Results: A total of 39 up- and 15 downregulated DEGs were screened. Most of the upregulated genes were involved in the immune response process, while the downregulated genes were involved in the steroid metabolic process. Moreover, we also found that HLA-A has the highest degree in the PPI network. The SP-D serum level and HLA-A gene frequency in COPD patients were significantly higher than those in healthy controls (13.62±2.09 ng/mL vs 10.28±2.86 ng/mL; 62.5% vs 12.5%; P <0.05).
Conclusion: Our results may help further the understanding of the mechanisms of COPD. The identified DEGs, especially HLA-A , may serve as diagnosis markers for COPD.
Keywords: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, differentially expressed genes, gene-ontology analysis, protein–protein interaction
Methods: The microarray raw dataset GSE29133, including three COPD samples and three normal samples, was obtained from Gene Expression Omnibus. After data preprocessing with the Affy package, Student’s t -test was employed to identify the differentially expressed genes (DEGs). The up- and downregulated DEGs were then pooled for gene-ontology and pathway-enrichment analyses using the Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery (DAVID). The upstream regulatory elements of these DEGs were also explored by using Whole-Genome rVISTA. Furthermore, we constructed a protein–protein interaction (PPI) network for DEGs. The surfactant protein D (SP-D) serum level and HLA-A gene frequency in COPD patients and healthy controls were also measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and real-time polymerase chain reaction, respectively.
Results: A total of 39 up- and 15 downregulated DEGs were screened. Most of the upregulated genes were involved in the immune response process, while the downregulated genes were involved in the steroid metabolic process. Moreover, we also found that HLA-A has the highest degree in the PPI network. The SP-D serum level and HLA-A gene frequency in COPD patients were significantly higher than those in healthy controls (13.62±2.09 ng/mL vs 10.28±2.86 ng/mL; 62.5% vs 12.5%; P <0.05).
Conclusion: Our results may help further the understanding of the mechanisms of COPD. The identified DEGs, especially HLA-A , may serve as diagnosis markers for COPD.
Keywords: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, differentially expressed genes, gene-ontology analysis, protein–protein interaction