109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
可生物降解的双纳米胶囊作为一种新颖的多功能载体用于药物递送和细胞成像
Authors Qian K, Wu J, Zhang E, Zhang Y, Fu A
Published Date June 2015 Volume 2015:10 Pages 4149—4157
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S83731
Received 1 March 2015, Accepted 27 April 2015, Published 25 June 2015
Approved for publication by Dr Lei Yang
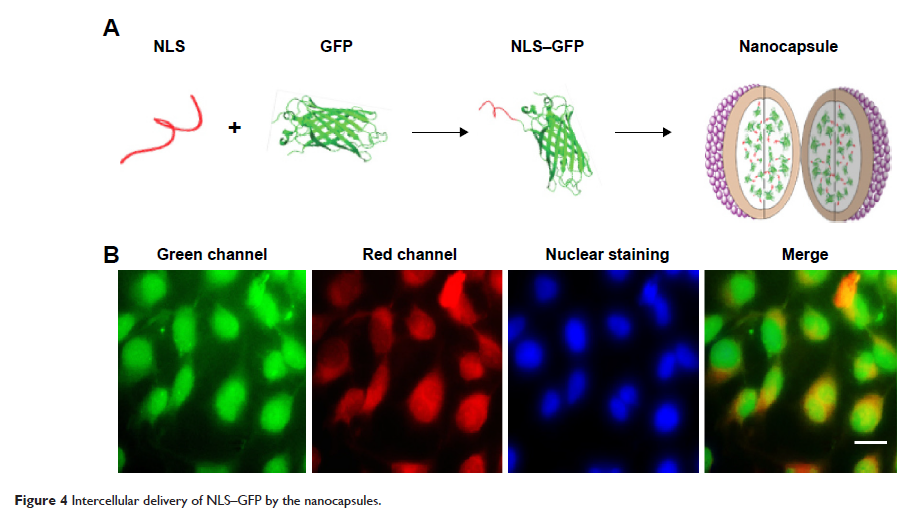
Abstract: Highly-efficient delivery of macromolecules into cells for both imaging and therapy (theranostics) remains a challenge for the design of a delivery system. Here, we suggested a novel hybrid protein–lipid polymer nanocapsule as an effective and nontoxic drug delivery and imaging carrier. The biodegradable nanocapsules showed the typical double emulsion features, including fluorescently labeled bovine serum albumin shell, oil phase containing poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) and linoleic acid, and inner aqueous phase. The nanocapsules were spherical in shape, with an average size of about 180 nm. Proteins packed into the inner aqueous phase of the nanocapsules could be delivered into cells with high efficiency, and the fluorescence of the fluorescently labeled bovine serum albumin could be used for tracing the protein migration and cellular location. Further studies suggested that the co-delivery of transcription factor p53 and lipophilic drug paclitaxel with the nanocapsules acted synergistically to induce Hela cell apoptosis, and the fluorescence of apoptotic cells was clearly observed under a fluorescence microscope. Such multifunctional delivery system would have great potential applications in drug delivery and theranostic fields.
Keywords: emulsion, protein transport, fluorescence labeling, theranostics, cell apoptosis
Keywords: emulsion, protein transport, fluorescence labeling, theranostics, cell apoptosis