109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
参芪解郁方 (Shen-Qi-Jie-Yu-Fang) 通过对免疫器官和T淋巴细胞亚群的调节,对产后抑郁症的啮齿动物模型有抗抑郁作用
Authors Qu M, Tang Q, Li X, Zhao R, Li J, Xu H, Gao Y, Mao Y
Published Date June 2015 Volume 2015:11 Pages 1523—1540
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S83964
Received 5 March 2015, Accepted 10 April 2015, Published 23 June 2015
Approved for publication by Professor Wai Kwong Tang
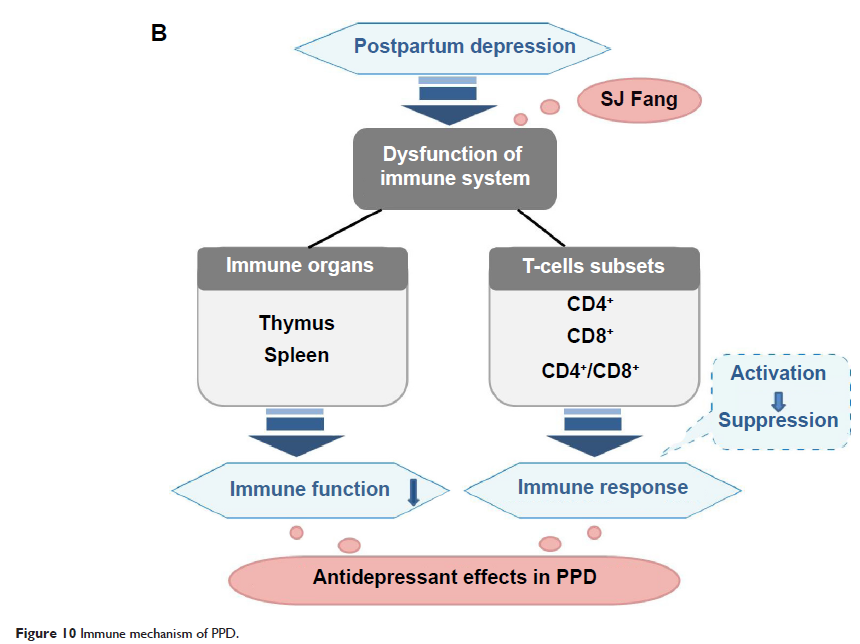
Background: Shen-Qi-Jie-Yu-Fang (SJ Fang) is a herbal preparation used in traditional Chinese medicine, and is a potentially important new therapeutic agent in postpartum depression (PPD). Previously, we have elucidated the effects of SJ Fang on hormone receptors and monoamine neurotransmitters involved in the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal and hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axes in PPD rats. However, the immune-modulating effects of SJ Fang in PPD are still unknown. In this study, we explored the effects of SJ Fang on the immune organs and subsets of T lymphocytes in PPD rats.
Methods: PPD was created in Sprague-Dawley rats by inducing hormone-simulated pregnancy followed by hormone withdrawal. After hormone withdrawal, the PPD rats were then treated with fluoxetine at 1, 2, and 4 weeks, and the SJ Fang rats were also treated at 1, 2, and 4 weeks. Depressive behavior in the rats was evaluated by the forced swim test, sucrose consumption test, and open field test. The thymus index and spleen index were calculated. Hematoxylin-eosin staining was used to identify pathological features in the thymus and spleen. CD3, CD4, and CD8 lymphocyte subsets were analyzed by flow cytometry.
Results: Both fluoxetine and SJ Fang decreased immobility time, increased sucrose consumption, an horizontal and vertical movement. After 4 weeks of treatment with fluoxetine or SJ Fang, the thymus index and spleen index were significantly higher than at baseline, and the morphology of the thymus and spleen were returning to normal. Two weeks after hormone withdrawal, subsets of T lymphocytes indicated a shift from immune activation to immune suppression, which was reversed by 4 weeks of treatment with fluoxetine or SJ Fang.
Conclusion: It is suggested that T-cell mediate immune responses which may play a role in the etiopathology of postpartum depression. SJ Fang had an antidepressant effect on the immune system in rats with PPD.
Keywords: spleen index, thymus index, Hematoxylin and eosin staining, CD4+/CD8+ ratio, immune activation, immune suppression
Methods: PPD was created in Sprague-Dawley rats by inducing hormone-simulated pregnancy followed by hormone withdrawal. After hormone withdrawal, the PPD rats were then treated with fluoxetine at 1, 2, and 4 weeks, and the SJ Fang rats were also treated at 1, 2, and 4 weeks. Depressive behavior in the rats was evaluated by the forced swim test, sucrose consumption test, and open field test. The thymus index and spleen index were calculated. Hematoxylin-eosin staining was used to identify pathological features in the thymus and spleen. CD3, CD4, and CD8 lymphocyte subsets were analyzed by flow cytometry.
Results: Both fluoxetine and SJ Fang decreased immobility time, increased sucrose consumption, an horizontal and vertical movement. After 4 weeks of treatment with fluoxetine or SJ Fang, the thymus index and spleen index were significantly higher than at baseline, and the morphology of the thymus and spleen were returning to normal. Two weeks after hormone withdrawal, subsets of T lymphocytes indicated a shift from immune activation to immune suppression, which was reversed by 4 weeks of treatment with fluoxetine or SJ Fang.
Conclusion: It is suggested that T-cell mediate immune responses which may play a role in the etiopathology of postpartum depression. SJ Fang had an antidepressant effect on the immune system in rats with PPD.
Keywords: spleen index, thymus index, Hematoxylin and eosin staining, CD4+/CD8+ ratio, immune activation, immune suppression