109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
VH 和 rhBMP-2 从纳米多孔镁-锌-硅干凝胶中缓释出来,用于骨髓炎治疗和骨修复
Authors Li FQ, Wu W, Xiang L, Weng G, Hong H, Jiang H, Qian J
Published Date June 2015 Volume 2015:10 Pages 4071—4080
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S82486
Received 9 February 2015, Accepted 28 March 2015, Published 22 June 2015
Approved for publication by Dr Lei Yang
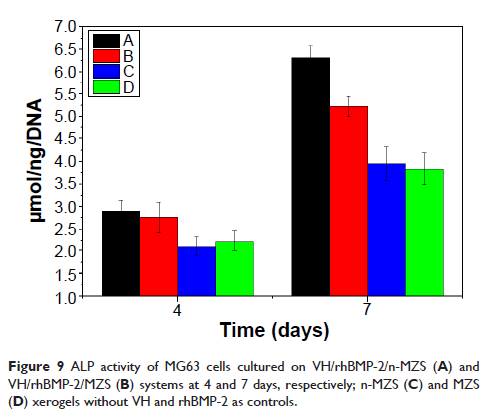
Abstract: Nanoporous magnesium–zinc–silicon (n-MZS) xerogels with a pore size of ~4 nm, a surface area of 718 cm2/g, and a pore volume of 1.24 cm3/g were synthesized by a sol–gel method. The n-MZS xerogels had high capacity to load vancomycin hydrochloride (VH) and human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (rhBMP-2), after soaking in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) for 24 hours (1.5 and 0.8 mg/g, respectively). Moreover, the n-MZS xerogels exhibited the sustained release of VH and rhBMP-2 as compared with magnesium–zinc–silicon (MZS) xerogels without nanopores (showing a burst release). The VH/rhBMP-2/n-MZS system not only exhibited a good antibacterial property but also promoted the MG63 cell proliferation and differentiation demonstrating good bactericidal activity and cytocompatibility. The results suggested that n-MZS with larger surface area and high pore volume might be a promising carrier for loading and sustained release of VH and rhBMP-2. Hence, the VH/rhBMP-2/n-MZS system might be one of the promising biomaterials for osteomyelitis treatment and bone repair.
Keywords: nanoporous xerogels, sustained release, drugs, osteomyelitis, bone regeneration, bactericidal activity, cytocompatibility
Keywords: nanoporous xerogels, sustained release, drugs, osteomyelitis, bone regeneration, bactericidal activity, cytocompatibility