9 7 8 1 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

对于呼吸机相关性肺炎,在降钙素原指导下停用抗生素:一项回顾性观察研究
Authors Wang Q, Hou D, Wang J, An K, Han C, Wang C
Received 15 October 2018
Accepted for publication 23 February 2019
Published 10 April 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 815—824
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S190859
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Joachim Wink
Background: Procalcitonin (PCT), an important
biomarker, can be used for the guidance of antibiotic therapy in respiratory
infection. However, it has been a problem that some patients might need
antibiotic therapy restart because of infection recurrence after antibiotic
discontinuation. To date, there are very few literature on the study of risk
factors accounting for infection recurrence. Purpose of this clinical study: 1)
To study on antibiotic discontinuation in ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP)
under the guidance of PCT; 2) To evaluate the possible risk factors leading to
infection recurrence and antibiotic reuse.
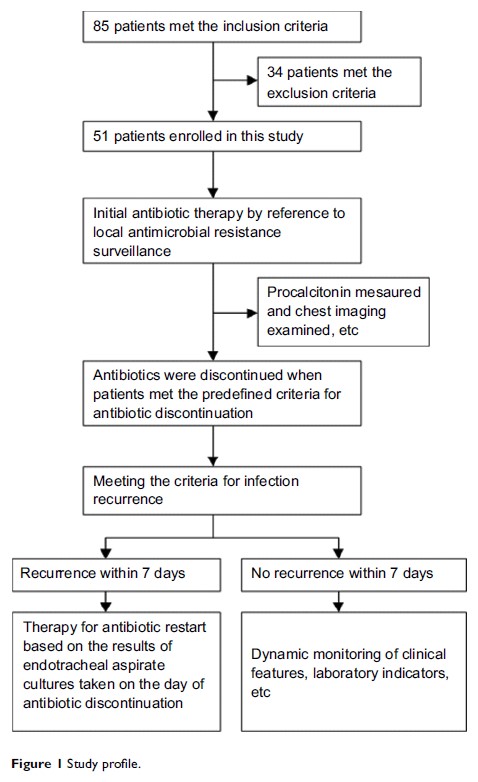
Methods: Antibiotic
discontinuation was performed when patients met the following criteria: (i)
serum PCT<0.5 μg/L, (ii) temperature<38.5℃ and (iii)
leukocyte count<15×109/L. Next, the
patients were divided into infection recurrence group (infection recurring within
7 days after antibiotic discontinuation) or infection controlled group (no
infection recurring after antibiotic discontinuation). Possible risk factors
accounting for infection recurrence were evaluated using logistic regression
analysis.
Results: Of
the eligible 51 patients with VAP, 20 patients suffered infection recurrence.
Clinical pulmonary infection score (CPIS) and characteristics of tracheal
secretions were the independent risk factors (P =0.045 and P =0.041,
respectively), accounting for infection recurrence. Simplified CPIS≥5 served a
certain predictive value for infection recurrence in VAP when physicians
considered antibiotic discontinuation (The area under the receiver operating
characteristic curve 0.781, specificity 90.3%, sensitivity 55.0%, positive
predictive value 78.6% and negative predictive value 75.7%). At the time of
antibiotic discontinuation, differences between the two groups were not
statistically significant in the proportion of patients with a tracheotomy and
in the culture results of endotracheal aspirates (including semi-quantitative
results and whether pathogens were multidrug-resistant [MDR] strains).
Conclusion: Simplified
CPIS and characteristics of tracheal secretions can be used to predict
infection recurrence following PCT-guided antibiotic discontinuation in VAP.
These findings are important because physicians may not need to put too much
care on semi-quantitative culture results of endotracheal aspirates and whether
pathogens are MDRstrains.
Trial registration: The registration number of this clinical trial is:
ChiCTR-OPC-17011228 (Trial registry name: Chinese Clinical Trial Registry; URL: http://www.chictr.org.cn).
Keywords: ventilator-associated
pneumonia, procalcitonin, antibiotic therapy, antibiotic discontinuation, infection
recurrence