9 7 8 1 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

胃蛋白酶原 C 过表达与人肝细胞癌预后不良有关:组织微阵列研究
Authors Chen H, Zhu HR, Yu XN, Shi X, Bilegsaikhan E, Guo HY, Huang RZ, Liu TT, Shen XZ, Zhu JM
Received 25 October 2018
Accepted for publication 7 March 2019
Published 10 April 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 2927—2934
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S192241
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Rituraj Purohit
Background: Aberrant
expression of pepsinogen C (PGC) has been observed in human cancers. However,
its role in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains to be established. The goal
of this study is to illustrate PGC expression and to evaluate its clinical
relevance in HCC.
Materials and methods: PGC
expression was examined in 75 pairs of HCC and adjacent non-tumor tissues using
tissue microarray. The correlations between its expression and clinical
parameters were also analyzed.
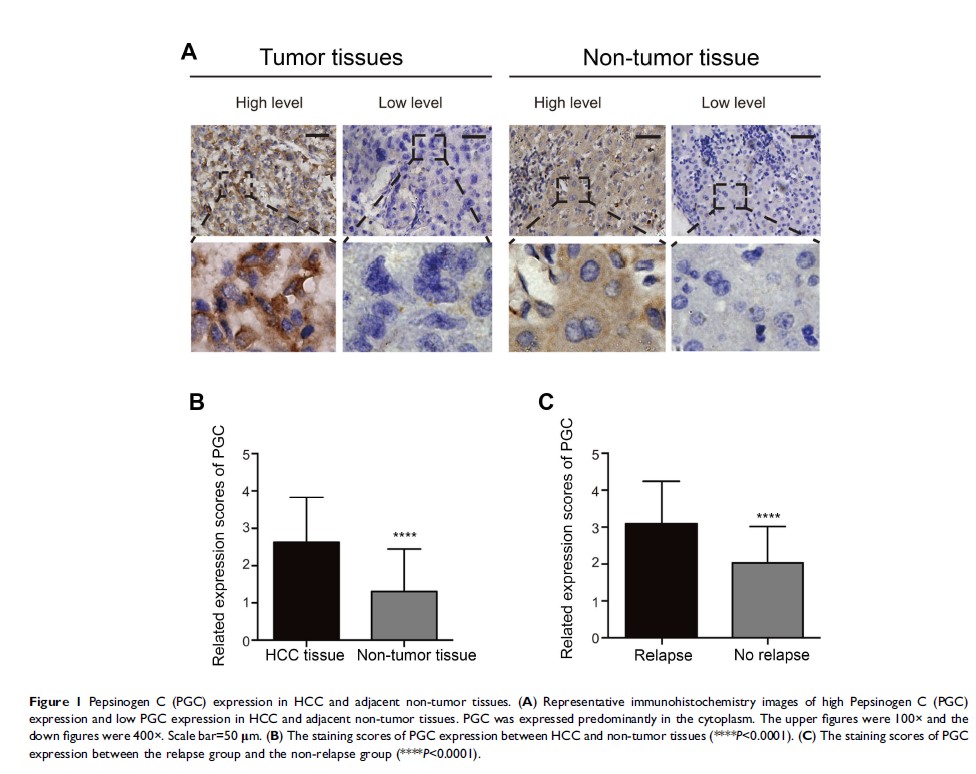
Results: PGC
overexpression was significantly associated with larger tumor size (≥5
cm; P =0.017)
and incomplete encapsulation (P <0.0001). Cox regression model demonstrated that
PGC expression and tumor size were independent prognostic factors for overall
survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) in HCC. The subgroup analysis by
Kaplan–Meier uncovered that OS and DFS were much worse in high PGC level group
than in low PGC level group with large tumor size subgroup, while no difference
of OS was noted between the two groups with low tumor size subgroup.
Conclusion: PGC plays
a tumorigenesis role in HCC progression, which may lead to a novel insight to
the potential biomarker and novel therapeutic strategies for HCC patients.
Keywords: hepatocellular
carcinoma, pepsinogen C, prognostic biomarker, tumor size, tissue microarray