9 7 8 1 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 通过靶向 miR-34a/ATG4B 通路增强奥沙利铂在结肠癌中的化疗耐药性
Authors Li Y, Li C, Li D, Yang L, Jin J, Zhang B
Received 20 September 2018
Accepted for publication 13 January 2019
Published 9 April 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 2649—2660
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S188054
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yao Dai
Purpose: The
chemoresistance of colon cancer to oxaliplatin (L-OHP) indicates poor
prognosis. Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) KCNQ1OT1 (KCNQ1 opposite
strand/antisense transcript 1) has been shown to participate in the
tumorigenesis of several types of cancers. However, little is known about the
role of KCNQ1OT1 in the chemoresistance and prognosis of colon cancer.
Materials and methods: Quantitative-PCR
and Western blot were used to measure the expression profiles of KCNQ1OT1,
miR-34a, and Atg4B in colon cancer tissues and cells. Cell viability assay and
flow cytometry were used to examine their effects on cell proliferation and
death. Cleavage of LC3 and GFP-LC3 plasmid transfection were used to detect
autophagic activity. Double luciferase reporter assay was used to verify the
interactions between miRNA and lncRNA or mRNA. Xenograft tumor model was used
to verify the effects of KCNQ1OT1 in vivo.
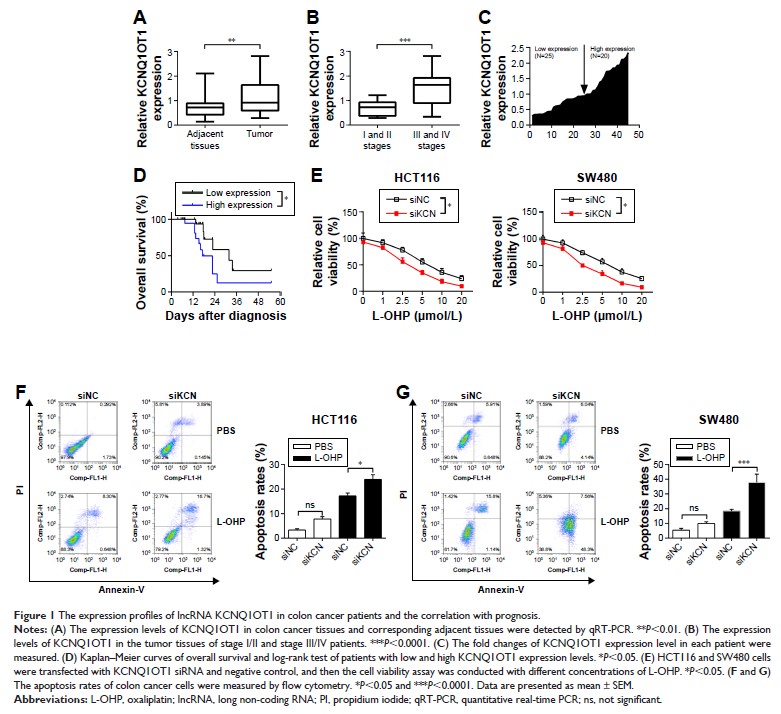
Results: In this
study, it is shown that the expression level of KCNQ1OT1 was increased in
tumor, which indicated poor prognosis in colon cancer patients. Using colon
cancer cell lines HCT116 and SW480, it was demonstrated that knockdown of
KCNQ1OT1 decreased the cell viability and increased the apoptosis rates upon
L-OHP treatment. Further studies indicated that Atg4B upregulation was
partially responsible for KCNQ1OT1-induced protective autophagy and
chemoresistance. Moreover, miR-34a functioned as a bridge between KCNQ1OT1 and
Atg4B, which could be sponged by KCNQ1OT1, while it could also bind to the
3'-UTR of Atg4B and downregulate its expressions. Finally, we show that the
KCNQ1OT1/miR-34a/Atg4B axis regulated the chemoresistance of colon cancer cells
in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusion: lncRNA
KCNQ1OT1 promoted the chemoresistance of colon cancer by sponging miR-34a, thus
upregulating the expressions of Atg4B and enhancing protective autophagy.
KCNQ1OT1 might become a promising target for colon cancer therapeutics.
Keywords: KCNQ1OT1,
colorectal cancer, protective autophagy, miR-34a, Atg4B, chemoresistance