108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

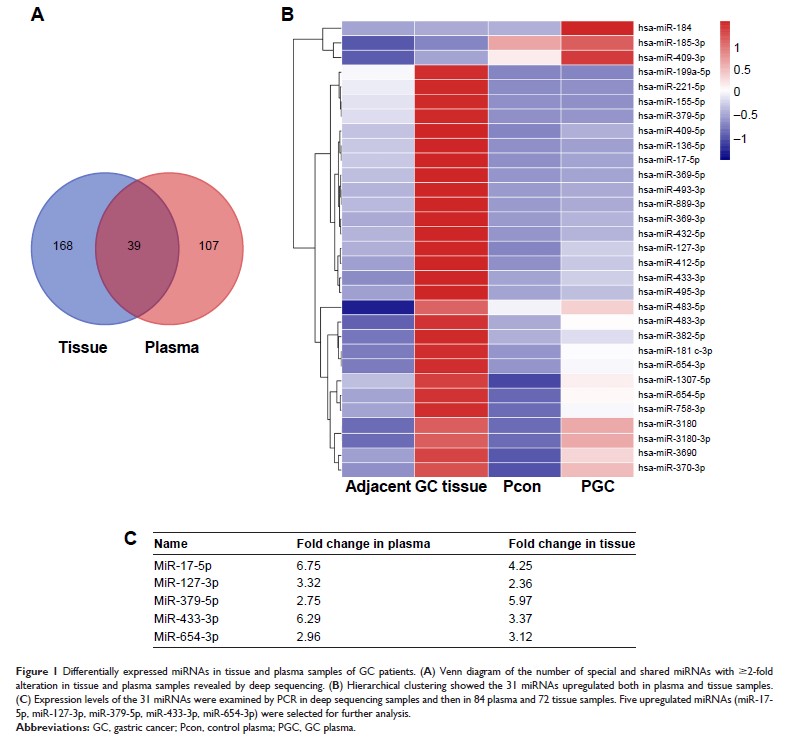
细胞游离 miR-17-5p 作为胃癌抑制树突细胞成熟的诊断生物标志物
Authors Cui ZJ, Xie XL, Qi W, Yang YC, Bai Y, Han J, Ding Q, Jiang HQ
Received 10 December 2018
Accepted for publication 15 February 2019
Published 9 April 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 2661—2675
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S197682
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Carlos E Vigil
Purpose: Gastric
cancer (GC) patients display aberrant miRNA expression and defective dendritic
cell function. However, the role of cancer cell-derived oncomiR in GC detection
and dendritic cell (DC) maturation remains largely elusive.
Methods: Candidate
miRNAs were selected by deep sequencing (8 GC plasma samples vs 8 control
plasma samples; 8 GC tissues vs 8 adjacent normal gastric tissues) and
confirmed by PCR with 164 plasma samples and 72 formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded
GC tissue samples. Their diagnostic performance was evaluated by receiver
operating characteristic curve. Cy3 fluorescence signals in DCs, exposed to
conditioned medium obtained from BGC-823 cells pre-transfected with
Cy3-miR-17-5p, were determined by flow cytometry and visualized by confocal
microscopy. Functional and phenotypical alterations of DCs were assayed when
DCs were transfected with miR-17-5p in vitro.
Results: Deep
sequencing and RT-PCR confirmed that five shared miRNAs were upregulated in
plasma and tissue samples of GC patients. Cell-free miR-17-5p was superior to
others in GC detection with an area under the curve of 0.82, and correlated
with lymphatic metastasis and poor overall survival. GC cell-shuttled miR-17-5p
can be delivered to immature DCs, and they significantly inhibited
LPS-stimulated phenotypic maturation by diminishing the expression of
maturation markers (MHC II, CD80 and CD86 molecules). In line with those
alterations in the phenotypic markers, functional experiments demonstrated that
miR-17-5p triggered an inhibitory effect on DCs endocytic activity and
decreased tumor necrosis factor-α and IL-12 secretion, while enhancing IL-10
production. Mixed lymphocyte reaction showed that miR-17-5p inhibited the T cell
stimulating effect of DCs and favored regulatory T cells expansion.
Conclusion: GC
cell-derived miR-17-5p is a potential biomarker for GC detection. Taken up by
DCs, miR-17-5p weakened antitumor immune responses via inhibiting the
maturation of dendritic cells.
Keywords: gastric
cancer, cell-free miRNA, biomarker, intracellular communication, dendritic cell